Figure 4.
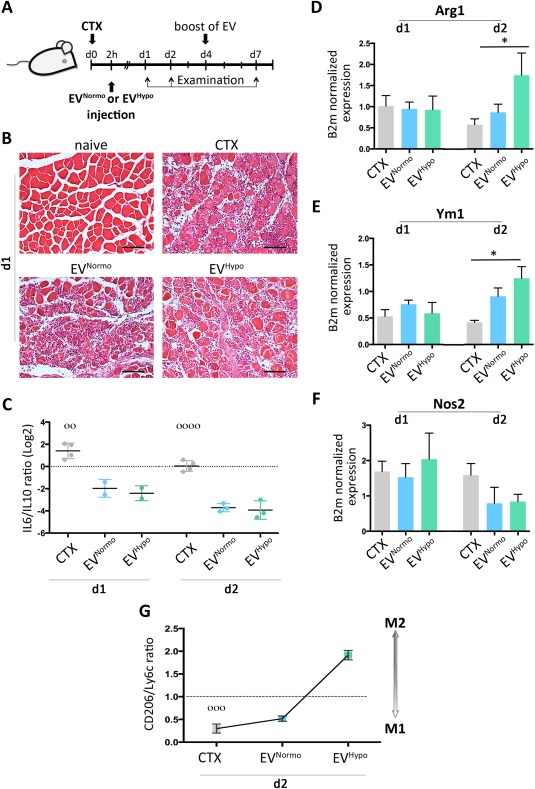
MSC‐derived EVs play direct effects on M1/M2 balance in a mouse model of cardiotoxin‐induced injury. (A): Schematic diagram of the experimental plan, illustrating the timelines of tibialis anterior (TA) muscle examination after CTX‐injury and EV‐injection. (B): Representative hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of TA muscles derived from naive C57Bl/6 mouse, CTX‐treated mouse (upper left and upper right panels, respectively), and from EVNormo‐ and EVHypo‐treated mice (bottom left and bottom right panels, respectively), one day after damage induction. Magnification ×20. Scale bar = 100 μm. (C): Quantitative real‐time PCR analysis of pro‐inflammatory (IL6) and anti‐inflammatory (IL10) cytokynes in TA muscles derived from mice treated with CTX (gray) alone or in combination with 1 μg EVNormo (light blue) or EVHypo (green), at 1 and 2 days post‐damage induction. Data are presented as log2 of mean expression ratio ± SEM. Statistical significance was determined using ANOVA. °°, p = .0024; °°°°, p < .0001. (D–F): Quantitative RT‐PCR for selected M1 (Nos2) and M2 (Arg1, Ym1) markers in CTX (gray), EVNormo (light blue) and EVHypo (green), at 1 and 2 days post‐CTX injury. B2m has been used as a housekeeping gene. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. Statistical significance was determined using ANOVA and Tukey's multiple comparisons test; (D) *, p = .0453. (E) *, p = .0087. (G): Flow cytometry analysis of MΦ subtypes recovered in the treated TA muscles (CTX, EVNormo and EVHypo) after 2 days. Data are presented as mean expression ratio between CD206 (M2) and Ly6C (M1). °°°, p = .0006 (ANOVA). Abbreviations: Arg1, Arginase 1; CTX, cardiotoxin; EVs, extracellular vesicles; Nos2, nitric oxide synthase 2.
