Figure 1.
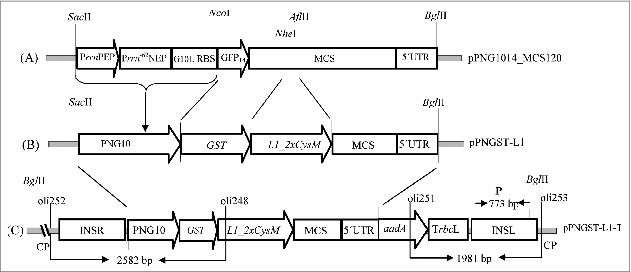
Schematic diagram of transformation vector construction (map not drawn to scale). (A) Precursor vector pPNG1014_MCS120 was used to clone transgenes. (B) Plasmid pPNGST-L1 obtained after the insertion of transgenes GST and L1_2xCysM in the precursor vector. (C) Final transformation vector pPNGST-L1-T for the transformation of plants, showing transgenes along with plastome flanks inserted within the tobacco plastid genome. PrrnPEP, plastid encoded polymerase promoter from rrn16 gene; Prrn-62NEP, nuclear encoded polymerase promoter; G10L RBS, ribosomal binding site from gene 10 leader sequence; GFP, first 14 amino acids of the green fluorescent protein; MCS, multiple cloning site; 5´ UTR, 5´ untranslated region; aadA, aminoglycoside 3'-adenylyltransferase; PNG10, cassette containing PrrnPEP, Prrn-62NEP and G10L RBS; CP, chloroplast DNA; GST, glutathione S-transferase gene; L1_2xCysM, modified L1 gene; TrbcL, terminator from large subunit of ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase gene; INSR, right insertion site (trnR); INSL, left insertion site (trnN).
