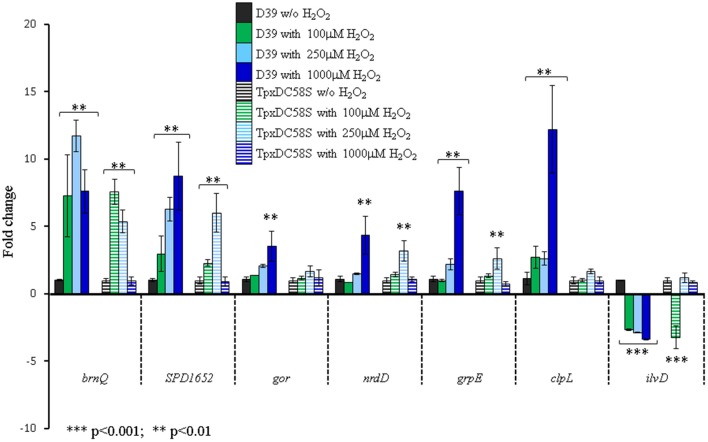
Figure 1.
TpxD scavenging activity is crucial for pneumococcal global response to high H2O2 levels. Seven genes identified in the microarray to be affected by 1 mM H2O2 were selected for further examination by relative RT-PCR. D39 and TpxDC58S mutant were grown anaerobically to OD620 = 0.25 and then challenged with 100, 250, or 1000 μM H2O2 for 40 min. Control cultures were grown without (w/o) the addition of H2O2. Values are the mean of duplicate determinations of at least two independent experiments, and were normalized to the expression level of the relevant unchallenged strain (D39 or TpxDC58S). Bars indicate standard deviation. Significant alterations in gene expression compared to bacteria grown without H2O2 were determined using Student's t-test.