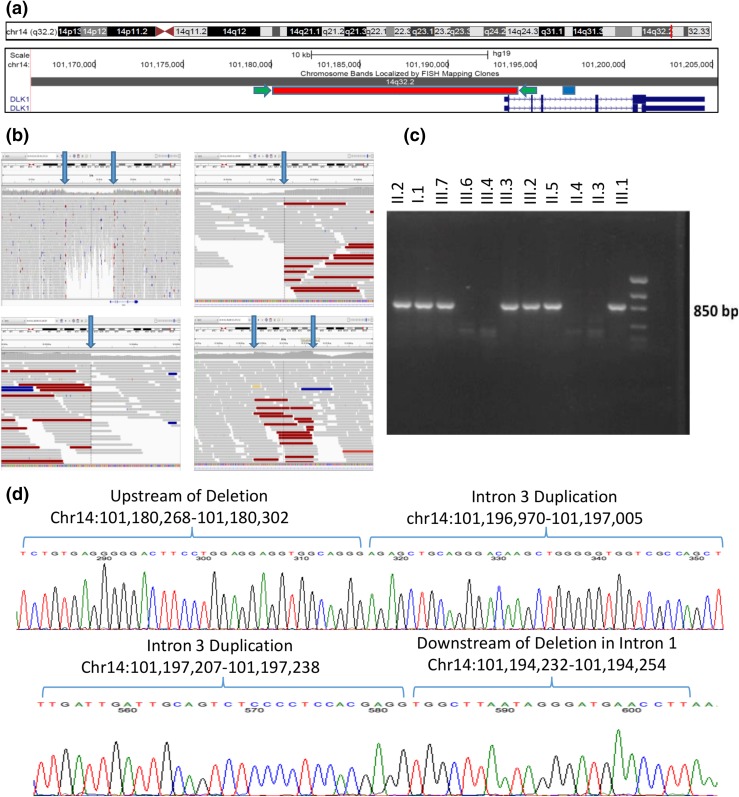
Figure 2.
Complex genomic rearrangement resulting in deletion of exon 1 of DLK1. (a) Screenshot of DLK1 region from the University of California Santa Cruz Genome Browser including two RefSeq DLK1 transcripts in dark blue. The region of the genomic deletion is highlighted in red, and the region of the duplication is highlighted in blue. The location of the PCR primers used to amplify the sequence of the deletion (c and d) are indicated by green arrows. (b) Screenshots from the Integrative Genomics Viewer of whole-genome data from subject III.2. In each panel, the top track lists the genomic coordinates shown on the screen. The middle section shows individual sequencing reads as gray bars with a histogram of individual base coverage above the reads. The colored reads represent individual paired-end sequence reads whose paired read is not located at the expected distance. This occurs due to the deletion/genomic rearrangement. Top left panel: overview of genomic region including DLK1 and its upstream region. The heterozygous deletion is clearly visible in the middle of the panel as a region of decreased sequencing coverage. The location of the DLK1 gene is noted at the bottom of this panel. Bottom left panel: zoomed-in view of the beginning of the deletion demonstrating a precipitous drop in sequencing coverage along with an abundance of reads with pairs at an unexpected distance. Top right panel: zoomed-in view of the end of the deletion. Bottom right panel: area of duplication in intron 3 of DLK1 showing increased coverage and abundance of reads with pairs at an unexpected distance. Blue arrows in all panels indicate the boundaries of the deletion or duplication. (c) PCR products demonstrating segregation of the deletion in the family. PCR primers span the deletion, and only individuals with the deletion demonstrate a PCR product of ∼850 bp. Subjects II.1, II.8, and III.5 were also tested and do not carry the deletion (data not shown). (d) Sanger sequencing of the PCR products in a subject with the complex genomic rearrangement. The sequence from intron 3 has been duplicated and inserted between the two ends of the large deletion. This results in a sequence that starts upstream of the deletion and then includes the whole duplicated region of intron 3 and concludes downstream of the deletion. The top panel’s sequence begins upstream of the deletion and shows the breakpoint where the upstream region joins the beginning of the duplicated region from intron 3 of DLK1. The bottom panel’s sequence starts with the end of the intron 3 duplicated region and joins to the region immediately downstream of the deletion in intron 1 of DLK1. All coordinates are given in the Genome Reference Consortium build 37.