Figure 4.
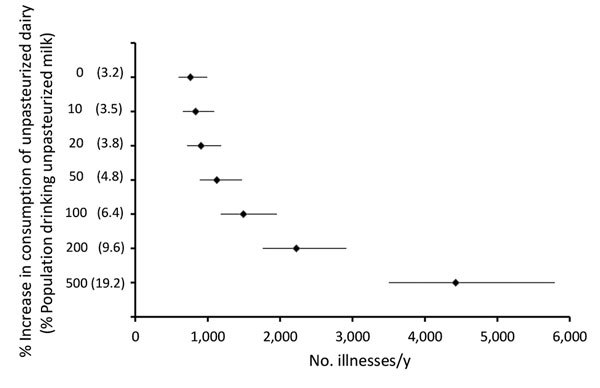
Number of dairy-related outbreak illnesses predicted per year in the United States if unpasteurized cow’s milk and cheese consumption increases 0%, 10%, 20%, 50%, 100%, 200%, and 500%. Numbers in parentheses indicate percentage of total population consuming unpasteurized cow’s milk. The illnesses graphed are those from outbreaks associated with cow’s milk or cheese contaminated with Shiga toxin–producing Escherichia coli, Salmonella spp., Listeria monocytogenes, and Campylobacter spp. Markers indicate means; bars indicate 95% prediction intervals. The consumption estimates were based on the year 2015, and a 0% increase corresponds to the current proportion of the US population consuming unpasteurized dairy products.
