Figure 1. Increased Lethality and Disease Activity in Il23RΔIEC Mice in Chronic Intestinal Inflammation.
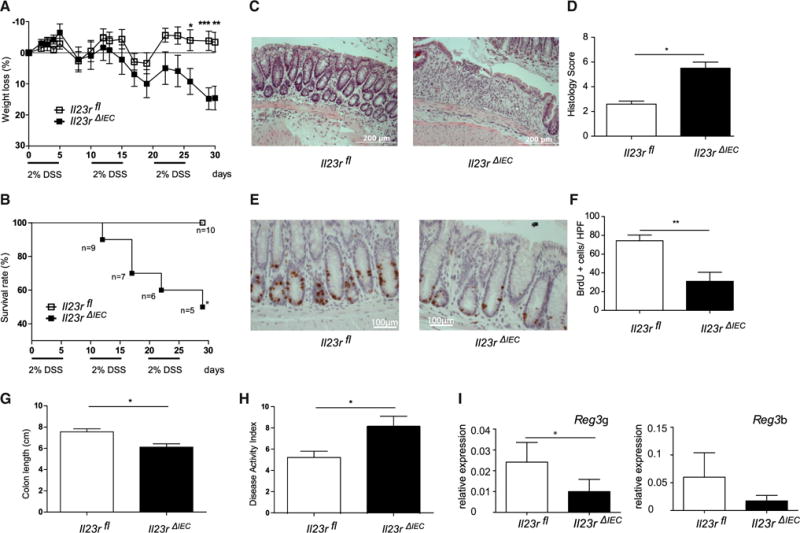
Colitis was induced by cyclic administration of 2% DSS (n = 10 male animals/group).
(A and B) Weight loss (A) and overall survival (B) were monitored every other day until day 30.
(C) Representative histologies (H&E) of DSS-treated Il23rΔIEC and Il23rfl mice on day 30.
(D) The histological score displays the combined score of inflammatory cell infiltration and tissue damage.
(E) Colonic sections from Il23rΔIEC and Il23rfl mice were immunostained with antibodies for BrdU.
(F) Positively stained cells were counted per high-power field (HPF, 4003).
(G) The columns represent the median of the colon length obtained from 10 animals/group postmortem on day 30.
(H) Overall disease activity index on day 30.
(I) Colon transcript levels of STAT3-dependent proliferation-associated Reg3b and Reg3g mRNA in Il23rΔIEC (n = 10 males) and IL23Rfl (n = 10 males) mice (qRT-PCR).
Significance was determined using two-tailed Student’s t test and is expressed as the mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
