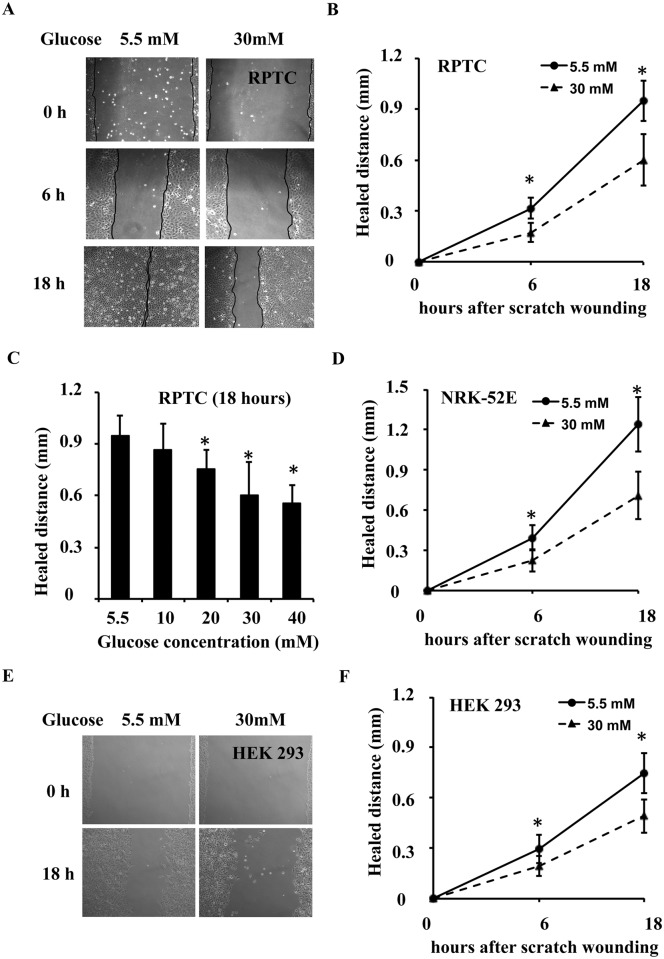
Fig 1. High glucose levels inhibit scratch-wound healing in cultured kidney tubular cells.
RPTC, NRK-52E and HEK 293 cells were cultured for 2 days in low glucose (5.5 mM) or high glucose (30 mM) medium, followed by a scratch-wound healing experiment. (A) RPTC were scratch-wounded with a sterile pipette tip and then incubated in low glucose or high glucose medium. Representative wounds immediately after scratching and after 6 and 18 h of healing were recorded with a phase-contrast microscope. (B) The wound width was measured at 6 and 18 h after scratching to determine the distance over which healing occurred in RPTC. (C) High glucose inhibited scratch-wound healing in RPTC in a concentration-dependent manner at 18 h after scratching. (D) NRK-52E were scratch-wounded with a sterile pipette tip and then incubated in low glucose or high glucose medium, the wound width was measured at 18 h after scratching. (E and F) HEK 293 were scratch-wounded with a sterile pipette tip and then incubated in low glucose or high glucose medium, the wound width was measured at 18 h after scratching. Data are expressed as the mean ± S.D. (n = 4). *, p<0.05 versus the low glucose group.