Figure 2.
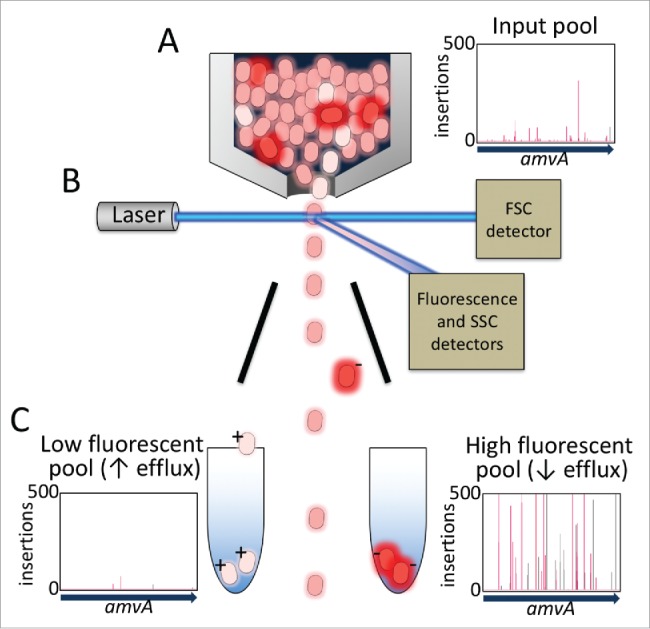
Overview of the TraDISort method for the physical enrichment of A. baumannii transposon mutants that have differentially accumulated ethidium bromide. (A) A mutant library pool is incubated with a low concentration of ethidium bromide and loaded onto a FACS instrument. The plot shows the density and frequency of insertions in the amvA gene, which encodes a major multidrug efflux pump, within the starting mutant pool. (B) Cells flow past the laser detection system and are screened for their ethidium content, size and granularity based on their light scattering and fluorescence properties. After screening the droplets containing only single cells break off from the flow stream and the droplets are differentially charged based on the fluorescence of the cell inside. (C) Cell droplets are sorted based on charge by deflection plates into high and low fluorescent pools, such that the most highly fluorescent cells (top 2%) are collected in one tube, and the most weakly fluorescent cells (bottom 2%) are collected in a second tube for extraction and TraDIS analysis. The plots show the locations and frequencies of insertions in amvA in the high and low fluorescent mutant pools.
