Figure 2.
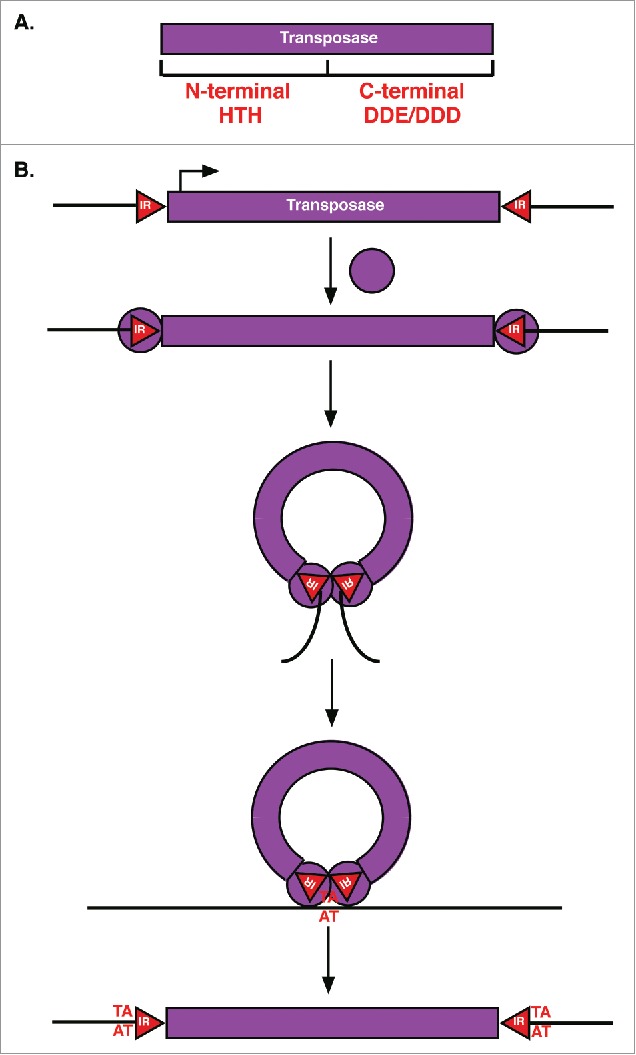
TIR transposase and transposition mechanism. (A) TIR Transposases have an N-terminal DNA binding domain with HTH motifs and a C-terminal DDE or DDD catalytic domain. (B) For transposition, TIR transposases (purple circles) first bind to inverted repeats (red triangles, IR) flanking the element. Bound transposases then dimerize followed by cleavage of the element from surrounding sequences (black lines) and integration into a new target site (AT) resulting in target site duplication.
