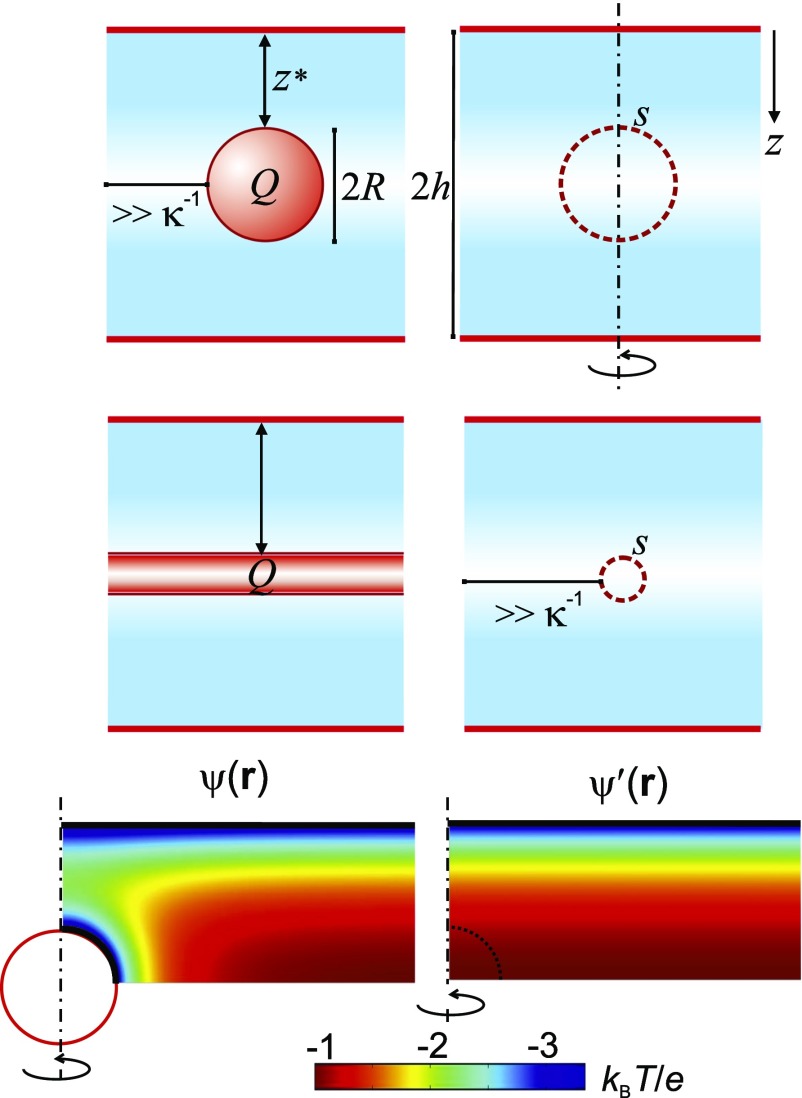
FIG. 4.
Schematic depiction of the interaction free energy method to calculate charge renormalization in macromolecules. The electrostatic potential distribution in an electrolyte-filled parallel-plate slit of height 2h is obtained by solving the non-linear Poisson-Boltzmann equation using constant charge boundary conditions, both with (left) and without the object (right). The average electrical potential in the slit is evaluated over the dashed circular contour representing the “virtual” surface of an object placed at (right). Electrostatic interaction free energies, , are calculated for an object of charge, Q, and radius, R, located at the mid-plane of the slit, at an inter-surface separation, , using the distribution (left) and Eq. (9). Dashed vertical lines denote axes of cylindrical symmetry.