Figure 2.
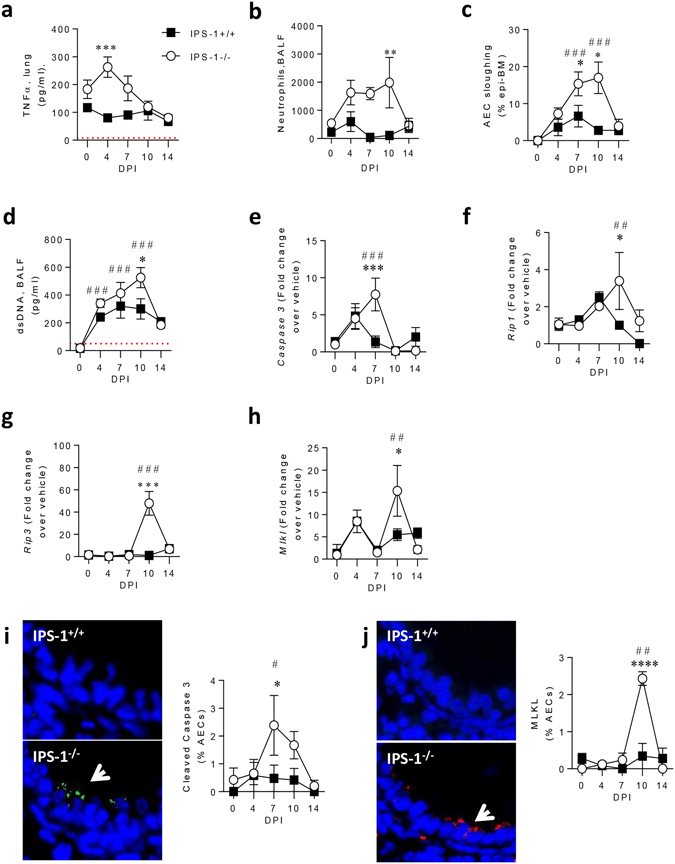
Absence of IPS-1 predisposes towards bronchiolitis and airway epithelial cell necroptosis during acute viral infection. (a) TNF-α protein expression in lung. (b) Neutrophil numbers in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF). (c) AEC sloughing represented as percentage of airway basement membrane. (d) dsDNA expression in BALF. Lung gene expression of (e) Caspase 3, (f) Rip1, (g) Rip3 and (h) MLKL. (i) Left panel: representative micrograph (100x magnification) of cleaved caspase 3 immunostaining. Right panel: Quantification of cleaved caspase 3 expression in AECs. (j) Left panel: representative micrograph (100x magnification) of MLKL immunostaining. Right panel: Quantification of cleaved MLKL expression in AECs. Experiments were performed twice with 6 to 8 mice per group. Vehicle control mice were sacrificed on day 7 of life (i.e. 0 dpi). Data are mean and the standard error of the mean. *,**,***,****Denotes significance between WT and IPS-1−/− infected mice. #,##,###Denotes significance between infected and vehicle IPS-1−/− mice. Detection limits are denoted by a red dotted line.
