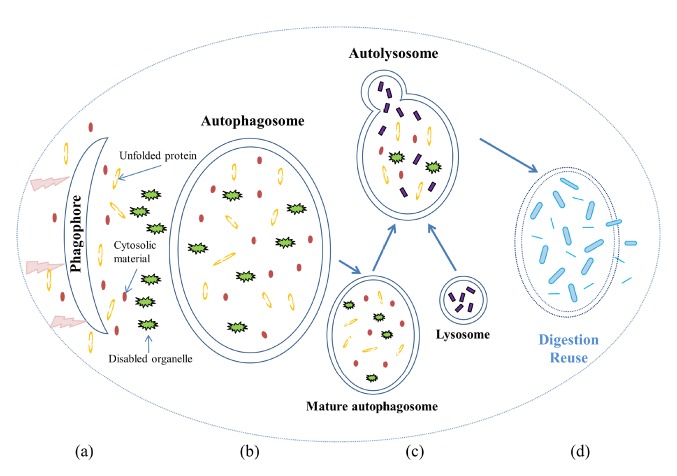
Figure 1.
Morphological process of autophagy. When a cell is experiencing starvation, the aggregation of unfolded proteins, a pathogen infection, or the accretion of any other cytotoxic factor, autophagy is initiated. (a) A flat bi-layer liposomal membrane known as the isolation membrane or phagophore forms in the cytosol. (b) As the membrane elongates, the phagophore seals itself to form an autophagosome that envelops the proteins, organelles, and other cytosolic material to be eliminated. The maturation of the autophagosome is coordinated with the endocytic system. (c) The mature autophagosome also fuses with the endosomal-lysosomal system, and lysosomal proteases are delivered to convert the autophagosome to an autolysosome. (d) The autolysosome digests the sequestered cytoplasmic material into amino acids and other molecules, which are reused after being transported across the membrane to the cytosol.