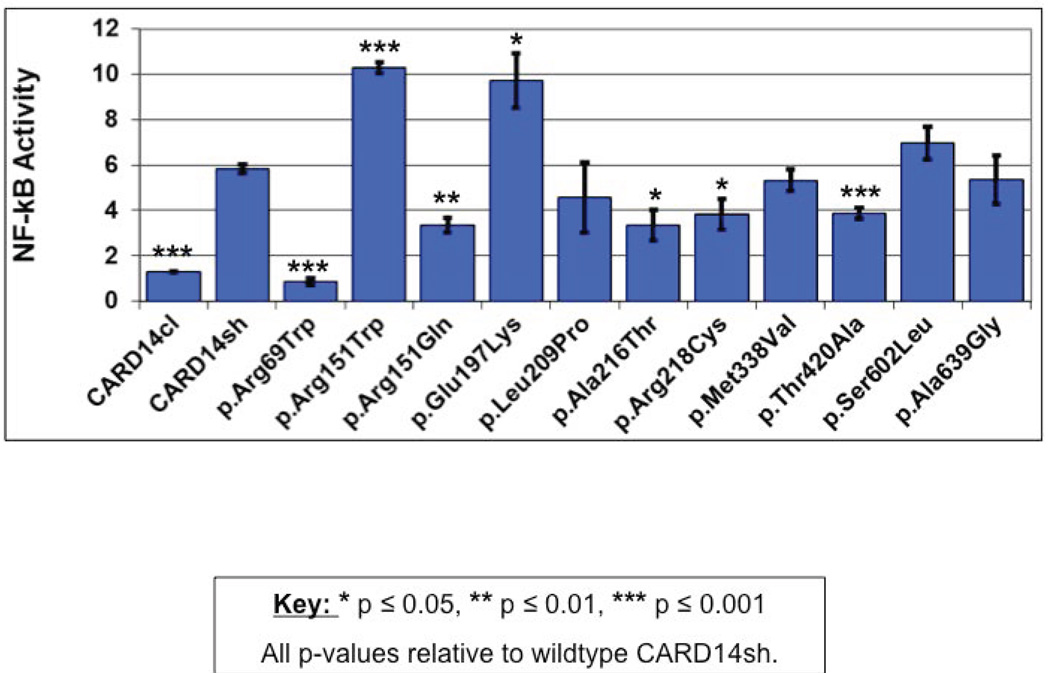
Figure 2. Effect of wild-type and novel CARD14 variants on NF-kb activation.
HEK293 cells were transfected with the construct that codes for wild type CARD14sh, the same construct harbouring one of the rare variants shown, or a construct that codes for CARD14cl and lacks the CARD domain. NF-kb activity was determined by measuring relative luciferase activity. All values were first normalized to Renilla expression to control for transfection efficiency and then adjusted to control for activity of the empty background vector, pTAL-luc. Change in NF-kb activity relative to background vector was determined for each variant (y-axis, NF-kb activity). Every data point represents the average of three replicates. Asterisks show results from two-tailed, unpaired student’s t tests comparing NF-kb activation induced by the indicated variant to that of unstimulated cells with CARD14sh. * p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.01, *** p ≤ 0.001.