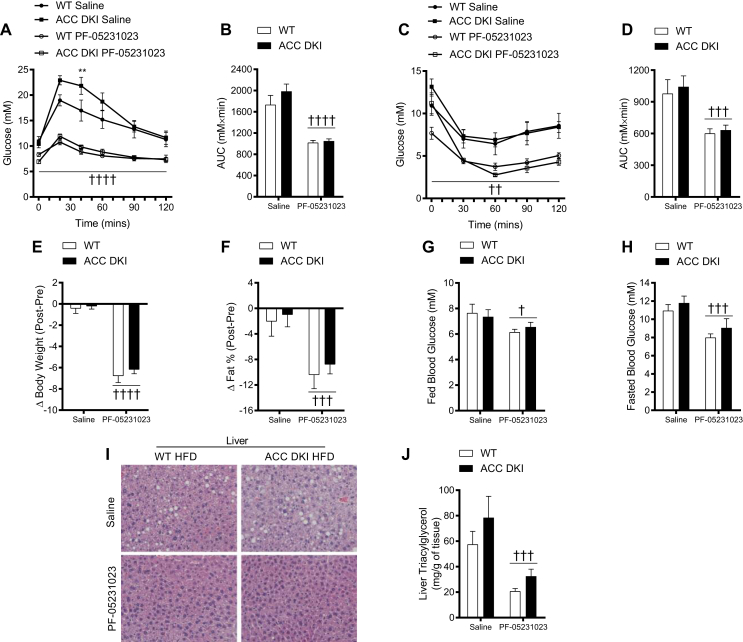
Figure 6.
Long-acting (PF-05231023) FGF21-mediated improvements in insulin sensitivity and hepatic lipid content are not due to AMPK's suppression of ACC. A–D: glucose tolerance test (GTT; 1 g/kg) (A) with area under the curve (AUC) (B) and insulin tolerance test (ITT; 1 U/kg) (C) with area under the curve (D) of wildtype and ACC DKI fed a 45% high fat diet for 10 weeks and treated with saline or long-acting FGF21 for two weeks (n = 4 per group). Change in body weights (E) and in fat percent (F) in wildtype and ACC DKI mice treated with saline or PF-05231023 (n = 8 per group). Blood glucose levels in the fed (G) and 12-hr fasted (H) state of wildtype and ACC DKI mice treated with saline or long-acting FGF21 for two weeks (n = 8 per group). I and J: representative H&E liver stains (20x) (I) and levels of triacylglycerol (J) in the liver of wildtype and ACC DKI mice treated with saline or long-acting FGF21 for 2 weeks (n = 8 per group). Data are means ± SEM with †††† p < 0.0001, ††† p < 0.001, †† p < 0.01, † p < 0.05 denoting a general treatment effect and ** p < 0.01 denoting a general genotype effect as determined by a two-way ANOVA (A and C: two-way repeated measures ANOVA).