TABLE 3.
Triazole MICs for Aspergillus species isolates carrying a mutated cyp51 gene, as determined by SYO and CLSI methodsa
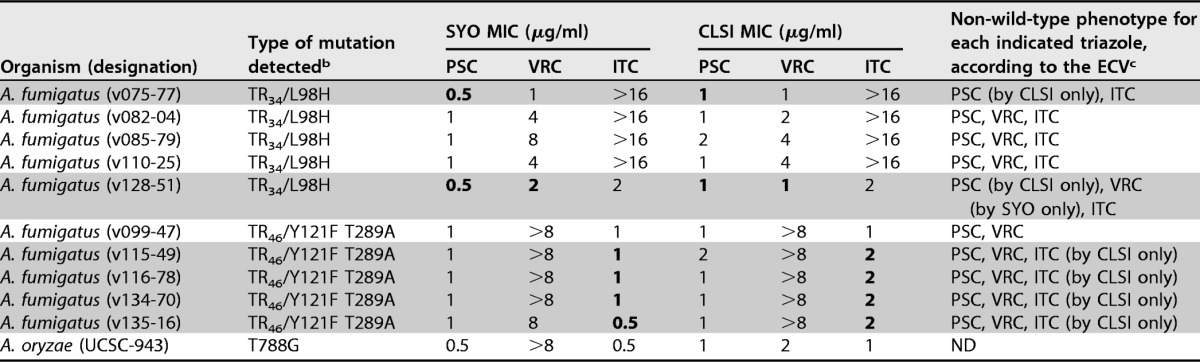
MICs of the triazoles posaconazole (PSC), voriconazole (VRC), and itraconazole (ITC) were determined as specified in the text (also see Tables 1 and 2 for details). MIC values of >16 μg/ml for itraconazole obtained by both methods were reported unchanged, whereas MIC values of ≥16 μg/ml for voriconazole obtained with the CLSI method were reported as >8 μg/ml, according to that specified in the text.
b Mutations occurring in the cyp51a gene of A. fumigatus and in the cyp51c gene (the homologue of cyp51a) of A. oryzae, which encode azole target enzyme, are indicated. The T788G missense mutation has been described, for the first time, in a clinical isolate of A. flavus (a species closely related to A. oryzae), with the data showing reduced in vitro susceptibility to voriconazole (MIC, 8 μg/ml) and itraconazole (MIC, 2 μg/ml) (22).
c ECVs were those published by Espinel-Ingroff et al. (10). Accordingly, PSC ECVs were used to identify non-wild-type (non-WT) isolates of A. fumigatus, A. terreus, and A. niger (ECV = >0.5 μg/ml), A. flavus (ECV = >0.25 μg/ml), and A. nidulans (ECV = >1 μg/ml); VRC ECVs were used to identify non-WT isolates of A. fumigatus, A. flavus, and A. terreus (ECV = >1 μg/ml) and of A. niger and A. nidulans (ECV = >2 μg/ml); and ITC ECVs were used to identify non-WT isolates of A. fumigatus, A. flavus, A. terreus, and A. nidulans (ECV = >1 μg/ml) and of A. niger (ECV = >2 μg/ml). Gray-shaded zones highlight those A. fumigatus isolates for which non-WT phenotypes were determined by only one of two methods (i.e., SYO or CLSI), where boldface denotes the MIC values that gave rise to the discrepancies between the methods. ND, not determined (because ECVs are lacking for the indicated species).
