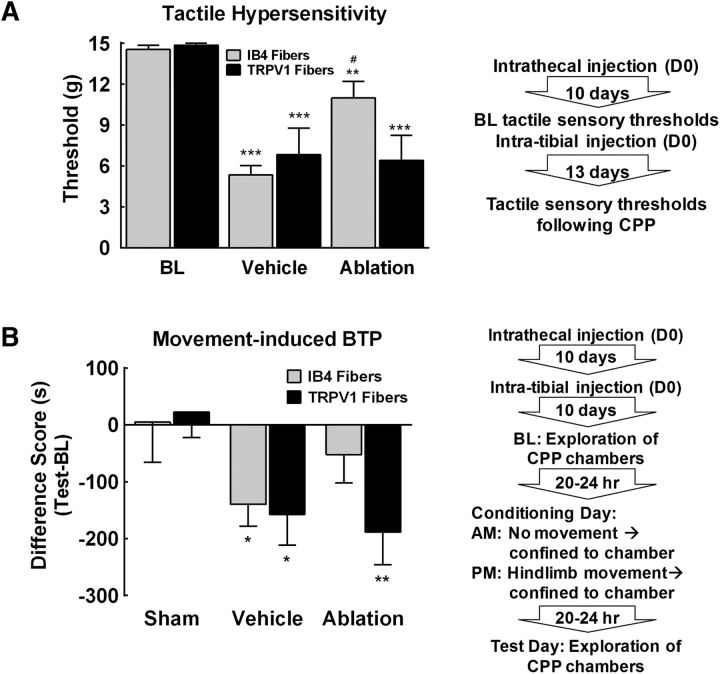
Figure 5.
Tactile hypersensitivity and movement-induced BTP is dependent on IB4 positive fibers. A, Spinal administration of IB4-SAP attenuated tumor-induced tactile hypersensitivity. Vehicle-treated tumor-bearing rats demonstrated tactile hypersensitivity with paw withdrawal thresholds significantly lower than precancer implantation baselines. ***p < 0.01 versus BL. Ablation of IB4-binding fibers by spinal administration of IB4-SAP attenuated tumor-induced tactile hypersensitivity, with paw withdrawal thresholds significantly higher compared with SAP control rats. #p < 0.05 versus SAP. Spinal ablation of TRPV1-expressing terminals in the spinal dorsal horn by spinal administration of capsaicin failed to eliminate tumor-induced tactile hypersensitivity, with paw withdrawal thresholds significantly lower than precancer baselines. ***p < 0.01 versus BL. B, Group comparison of difference scores demonstrates that movement induced CPA in vehicle-treated rats compared with sham controls. *p < 0.05 versus sham. Ablation of IB4-binding fibers blocked movement-induced CPA. In contrast, ablation of TRPV1-expressing terminals in the spinal dorsal horn failed to block movement-induced CPA. **p < 0.01 versus shams. Graphs are mean ± SEM. Sham, n = 10 capsaicin, n = 10 IB4-SAP; cancer, n = 9 SAP, n = 8 capsaicin vehicle, n = 11 IB4-SAP, and n = 10 capsaicin.