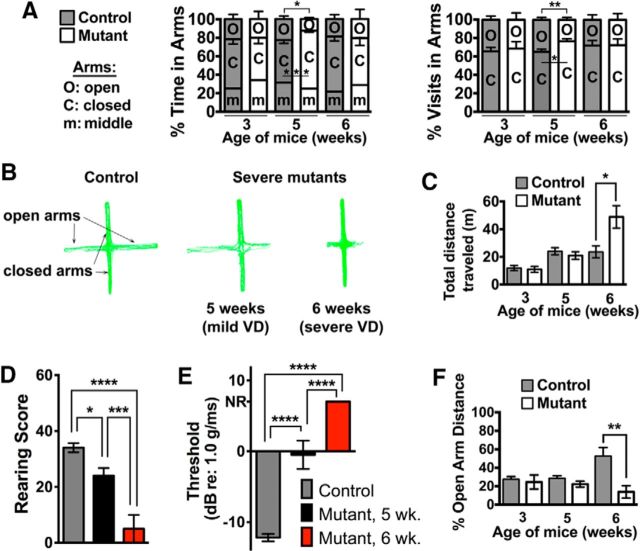
Figure 7.
Minor VD promotes anxiety symptoms, whereas major VD promotes hyperactivity in Tbx1Cre/+;Slc12a2fx/fx mutants. A, EPM testing shows that 3-week-old mutants exhibit normal anxiety. At 5 weeks, severe mutants begin showing subtle VD and spend more time in and make more visits to the closed arms. At 6 weeks, severe mutants have extensive VD and resume normal anxiety levels. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 3 or 4 mice/genotype at 3 weeks; n = 8 or 9 mice/genotype at 5 weeks; n = 6 mice/genotype at 6 weeks). Five weeks in arms: *p = 0.0126, ***p = 0.0005; 5 week visits in arms: **p = 0.01, Student's two-tailed test. B, Representative EPM traces of control and mutants. C, Total distance traveled during EPM testing. Severe mutants in A become hyperactive at 6 weeks. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 3 or 4 mice/genotype at 3 weeks; n = 8 or 9 mice/genotype at 5 weeks; n = 6 mice/genotype at 6 weeks). *p = 0.0202, Student's two-tailed test. D, E, Rearing analysis (D) and VsEPs (E) indicate minor VD in mutants at 5 weeks and major VD at 6 weeks. NR, No response. Data are mean ± SEM (D; control: n = 17; 5 week mutant: n = 8; 6 week mutant: n = 7; E; control: n = 9; 5 week mutant: n = 3; 6 week mutant: n = 6). *p = 0.0329, one-way ANOVA with Tukey multiple-comparisons test. ***p = 0.0007, one-way ANOVA with Tukey multiple-comparisons test. ****p < 0.0001, one-way ANOVA with Tukey multiple-comparisons test. F, Tbx1Cre/+;Slc12a2fx/fx mutants with major VD travel significantly shorter distances in the open arms of the EPM at 6 weeks of age. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 3 or 4 mice/genotype at 3 weeks; n = 8 or 9 mice/genotype at 5 weeks; n = 6 mice/genotype at 6 weeks). **p = 0.0017, Student's two-tailed test.