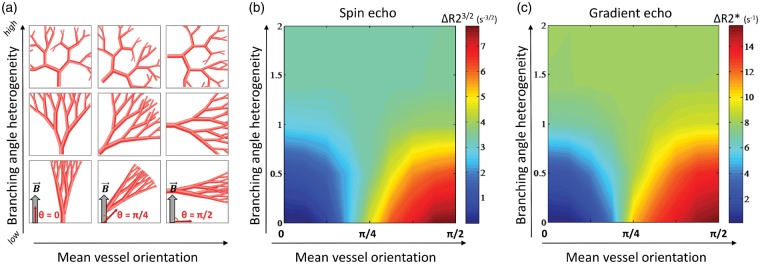
Figure 3.
The effects of vessel orientation distributions on the relaxation rates. Illustrations of white matter-like vessel trees (a) with increasing mean vessel orientation relative to the main magnetic field (left to right) and increasing branching angle heterogeneity (bottom to top). The resulting relaxation rates from spin echo (b) and gradient echo (c) are independent of mean vessel orientation when branching angle heterogeneity is high (σ > 1). With lower branching angle heterogeneity (σ < 1), the relaxation rates increase when mean vessel orientation approaches π/2.