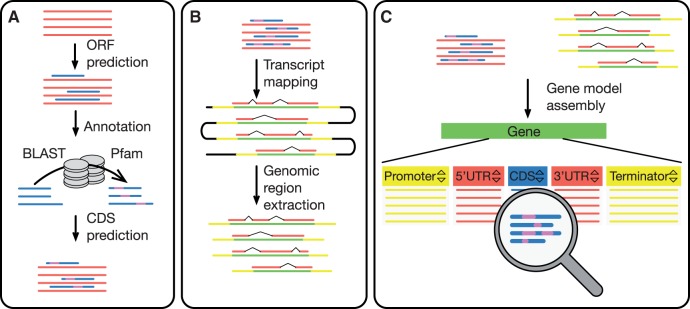
Fig. 1.
Data preparation and assembly. Red stripes denote the transcripts; blue stripes denote CDSs and corresponding proteins; purple stripes denote Pfam and BLAST annotation; yellow stripes denote 3 Kb regions which flank transcript mapping sites on a genome; black stripes denote a genome sequence. (A) Prediction of CDSs and annotation: The longest ORFs were predicted using TransDecoder software. Corresponding protein sequences were annotated using BLAST to a Uniprot protein database and Pfam signature analysis. (B) Extraction of genomic sequences: Transcripts, which passed annotation and CDS prediction analysis, were mapped to the genome assembly using Splign software. Genomic regions, which corresponded to the transcript mapping sites, were extracted together with 3 Kb flanking regions, to account for potential promoter sequences. (C) Assembly of the gene models: Information about transcript mapping sites, CDSs, protein annotations, and extracted genomic regions were assembled into a gene model, where each gene is an assembly of a promoter, transcript and terminator. Every gene stores a relative genomic location, based on its mapping site.