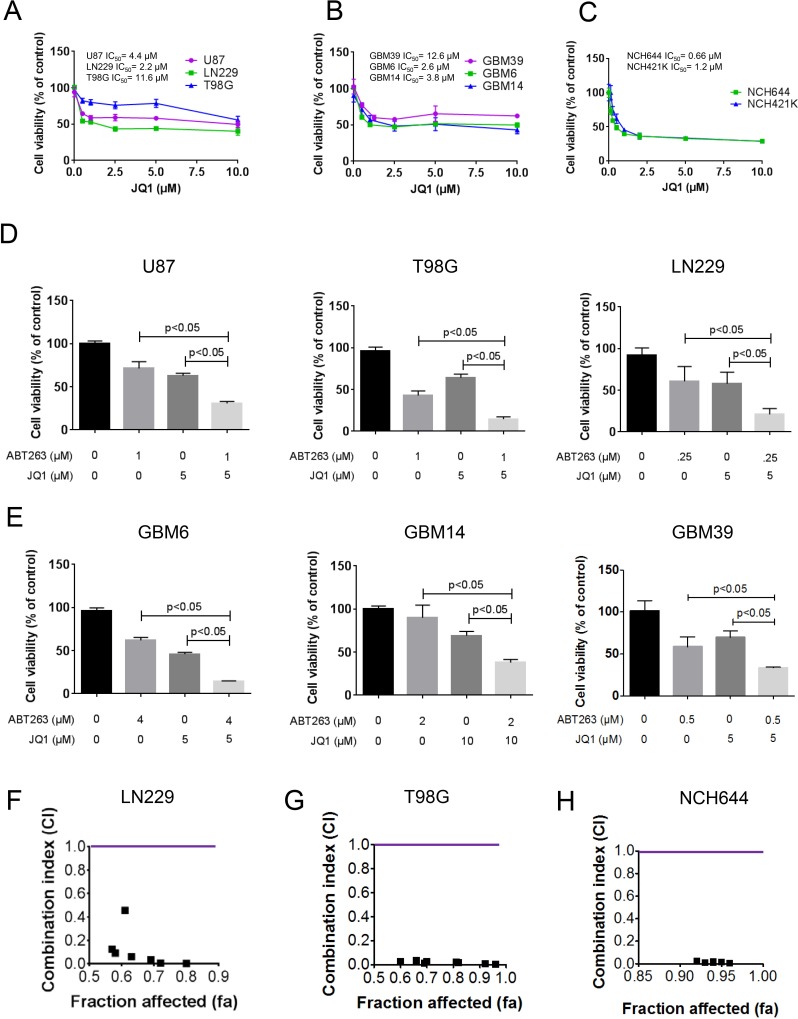
Figure 1. Combined treatment with ABT263 and the BET-inhibitor (JQ1) results in a synergistic antiproliferative effect across a wide spectrum of human glioma cells.
A.-C. U87MG, LN229, T98G established glioblastoma cell lines, GBM39, GBM6 and GBM14 patient-derived xenograft cultures and NCH644 and NCH421k stem cell-like glioma cultures were treated as indicated with JQ1. After 72h of treatment, CellTiter-Glo assays were performed. IC50 values were calculated. Column: mean. Error bar: standard deviation (SD). n = 3. D., E., U87MG, LN229, T98G established glioblastoma cell lines, GBM39, GBM6 and GBM14 patient-derived xenograft cultures were treated with ABT263, JQ1 or the combination of both. After 72h of treatment, CellTiter-Glo assays were performed. Column: mean. Error bar: standard deviation (SD). n = 3. Statistical analysis was performed and p values were calculated. A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. F.-H., LN229, T98G and NCH644 glioblastoma cells were treated for 72 hours with ABT263, JQ1 or the combination and analyzed by CellTiter-Glo assay. CI values and fraction affected were calculated using the CompuSyn software (ComboSyn, Inc., Paramus, NJ, U.S.A.). Data points located below 1 (CI value less than 1) indicate a synergistic drug-drug interaction and data points larger than 1 indicate an antagonistic drug-drug interaction. Some data points overlap and are therefore not represented on the graphical chart. A colored line highlights CI value 1. For individual values, please refer to Table 1.