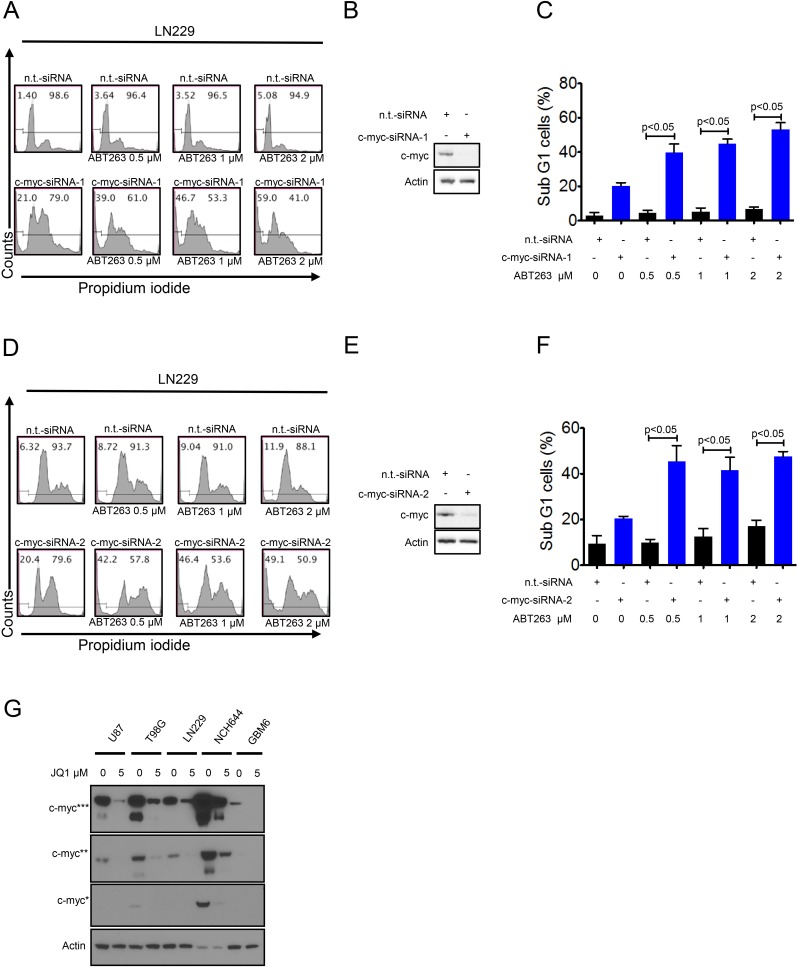
Figure 5. Silencing of c-myc sensitizes for Bcl-xL inhibition.
A., LN229 cells were transfected with n.t.-siRNA or c-myc-siRNA-1 prior to treatment with solvent or ABT263 as indicated for 24 h. Staining for propidium iodide and flow cytometric analysis were performed to determine the fraction of subG1 cells. Representative flow plots are shown. The quantifications are shown in C. c-myc knockdown was confirmed by Western blot analysis B. D., LN229 cells were transfected with n.t.-siRNA or c-myc-siRNA-2 prior to treatment with solvent or ABT263 as indicated for 24 h. Staining for propidium iodide and flow cytometric analysis were performed to determine the fraction of subG1 cells. Representative flow plots are shown. The quantifications are shown in F. c-myc knockdown was confirmed by Western blot analysis E. G. U87, T98G, LN229 (established glioblastoma cells), NCH644 (stem cell-like glioma cells) and GBM6 (patient-derived xenograft) cells were treated with JQ1 for 72 hours. Protein extracts were prepared and samples were analyzed by conventional western blot analysis for the expression of c-myc. Actin serves as a loading control. Multiple exposures are presented due to the fact that cells express different baseline levels of c-myc. * indicate different exposure times for c-myc protein.