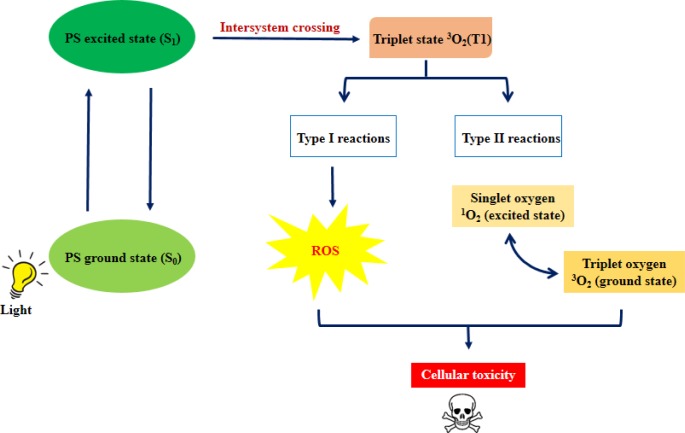
Figure 1. Mechanism of PDT.
Upon light activation, the photosensitizer is excited (S0 to S1). S1 is converted to a more stable triplet state via intersystem crossing. Further, type I reactions involve the formation of ROS, whereas, the loss of energy in type II reactions leads to the formation of highly reactive singlet oxygen species; ultimately leading to cellular toxicity.