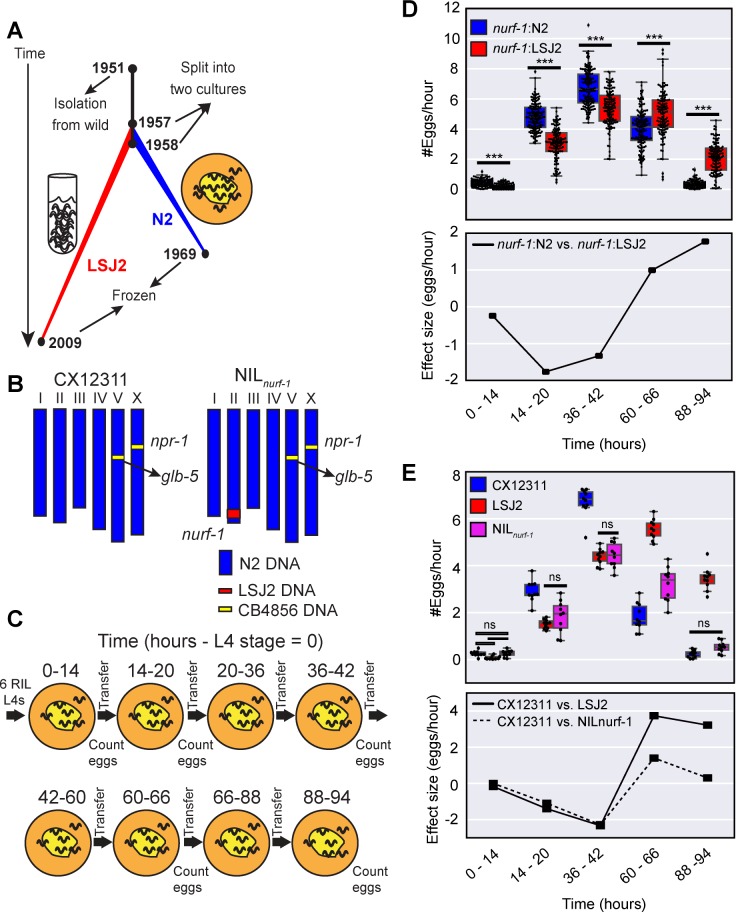
Fig 1. A major-effect QTL has an age-dependent effect on egg-laying.
A. History of two laboratory strains of C. elegans (N2 and LSJ2) following isolation of a single hermaphrodite individual from mushroom compost collected in Bristol, England in 1951. LSJ2 was grown in liquid, axenic culture whereas N2 was propagated on agar plates. B. Schematic of CX12311 and NILnurf-1 strains. CB4856 is a wild strain isolated from Hawaii. N2 contains two fixed mutations in the npr-1 and glb-5 genes. To avoid studying their effects, we backcrossed the ancestral alleles of these genes from CB4856 into the N2 strain. NILnurf-1 contains a small region surrounding nurf-1 backcrossed from LSJ2 into CX12311. C. Schematic of the experiments used to characterize the egg-laying rate at five time points. t = 0 was defined as the start of the L4 stage. D. Top panel. All egg-laying rate data of 94 RIL strains created between the CX12311 and LSJ2 strains. Animals were partitioned based upon their nurf-1 genotype (blue = N2; red = LSJ2). The small difference in x-axis values for the two backgrounds are for illustration purposes only and do not indicate differences between measurements of egg-laying rate. Overlaid is a boxplot showing the quartiles of the data (the box) with the whiskers extended to show the rest of the distribution except for points determined to be outliers. All scatterplots and boxplots in the subsequent figures were calculated in the same way. For all figures, ns p >0.05, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 by Mann-Whitney U test with Bonferroni correction. Bottom panel. The effect size of the nurf-1 locus measured from the RIL strains. E. Top panel. The egg-laying rate of CX12311, LSJ2, and NILnurf-1 strain measured at five time points. For just this figure, only non-significant differences are shown. All other comparisons are significant at p < 0.05. Bottom panel. Effect size of the nurf-1 locus measured from the NIL and parental strains.