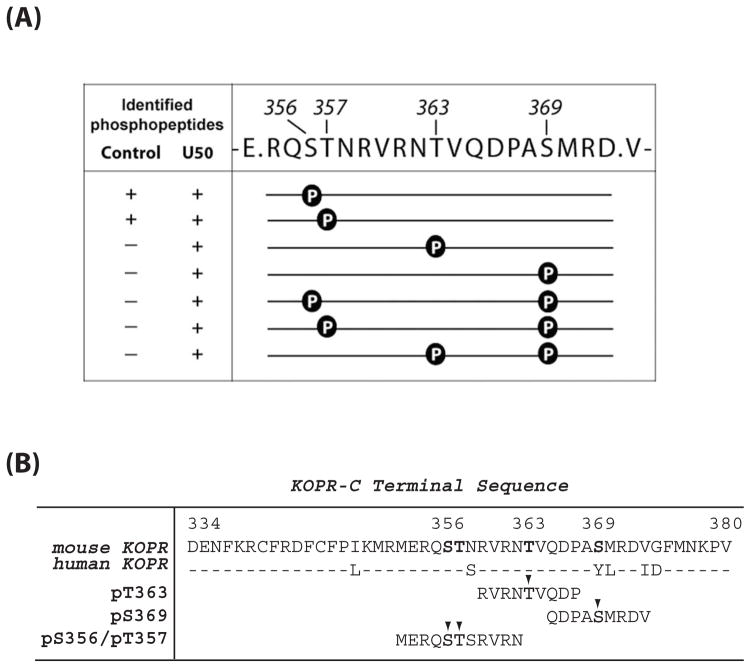
Figure 1. (A) Sites of U50,488H-induced phosphorylation in the mouse KOPR.
N2A-FmK6H cells were treated with vehicle or 10 μM U50,488H at 37°C for 30 min. The receptor was purified using a Ni-NTA agarose column followed by an anti-FLAG M2 antibody-agarose affinity column. Eluates were resolved with SDS-PAGE and the KOPR bands were excised and in-gel digested with the endopeptidase Glu-C and subject to LC-MS/MS. Glu-C cuts at the C-terminal to Glu and Asp. The fragment shown here contains all the possible Ser and Thr phosphorylation sites in the C-terminal domain. Data were analyzed with Peaks Studio 6.0. The presence and absence of the phosphopeptide in the samples are indicated by “+” and “−“, respectively. The results were pooled from two experiments.
(B) Sequence of C-terminal domain of the mouse and human KOPRs and sequences of the phosphopeptides used as the antigens for antiserum generation. The phosphorylated residues are indicated with arrow heads.