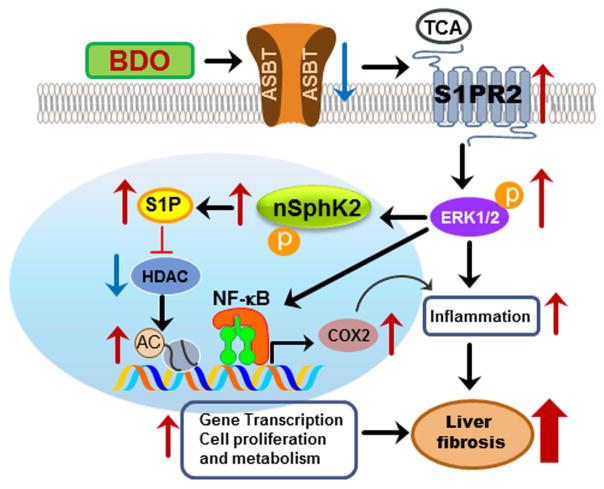
Figure 8. Model of bile duct obstruction-induced liver fibrosis.
Bile duct obstruction (BDO) induces inflammation and CBAs, mainly TCA, in the liver. BDO-induced inflammation down-regulates apical sodium dependent bile acid transporter (ASBT) and upregulates S1PR2 in cholangiocytes. Extracellular TCA activates S1PR2, which further activates the ERK1/2-SphK2 signaling pathway. Activation of nuclear SphK2 increases the levels of S1P in the nucleus, which further inhibits specific histone deacetylases (HDACs) resulting in an increase in acetylation of histones and up-regulation of genes involved in cell proliferation and metabolism. Activation of ERK1/2 also induces activation of NF-κB and increases COX-2 expression. CBA-induced S1PR2 activation plays a critical role in cholestasis-induced liver injury.