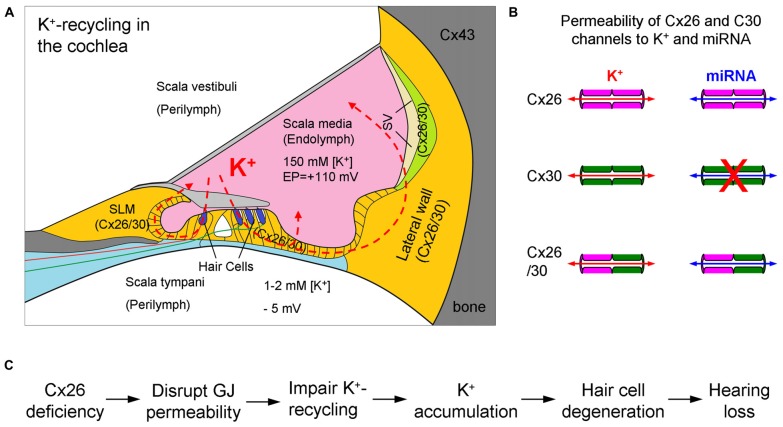
Figure 1.
K+-recycling in the cochlea and hypothesized deafness mechanism of Cx26 deficiency. (A) Cochlear structure and K+-recycling pathways in the cochlea. Cx26 and Cx30 colocalized in most cochlear tissues and cells but not in hair cells. SLM, spiral limbus; SV, stria vascularis. Modified from Forge et al. (2003), Zhao and Yu (2006) and Liu and Zhao (2008). (B) Permeability of Cx26 and Cx30 gap junctional channels to ions and small molecules. Cx30 channels are impermeability to negative charged molecules, such as miRNAs. Based on Yum et al. (2010) and Zong et al. (2016). (C) The hypothesized K+-recycling defect as a mechanism for Cx26 deficiency induced hearing loss. GJ, gap junction.