Fig. 2.
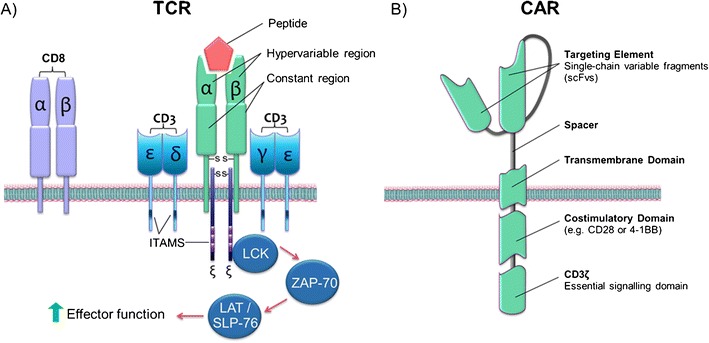
Structure of TCRs and CARs. a The TCR is comprised of α and β chains that closely associate with the ε-δ-γ- and ζ-chains of the CD3 complex. Antigen-mediated activation of the α/β chains induces phosphorylation of the ITAMs by LCK. Subsequent activation of ZAP-70 and its downstream targets, LAT and SLP-76, induces an intracellular signaling cascade resulting in the upregulation of genes associated with T cell effector function. (reprinted from Lineberry N, Fathman GC: Immunity 2006, 24(5):501–503, with permission from Elsevier) [46]. b Design of the chimeric antigen receptor includes the single-chain variable fragment with antigen-binding affinity, fused to a spacer and transmembrane domain. Effector function is conferred via the TCR CD3ζ domain, while the addition of one (2nd generation) or two (3rd generation) costimulatory domains drives signal activation and amplification of various effector signaling cascades (with permission from Juno Therapeutics: Chimeric Antigen Receptor Technology (CARs) https://www.junotherapeutics.com/our-science/car-technology/) [47]
