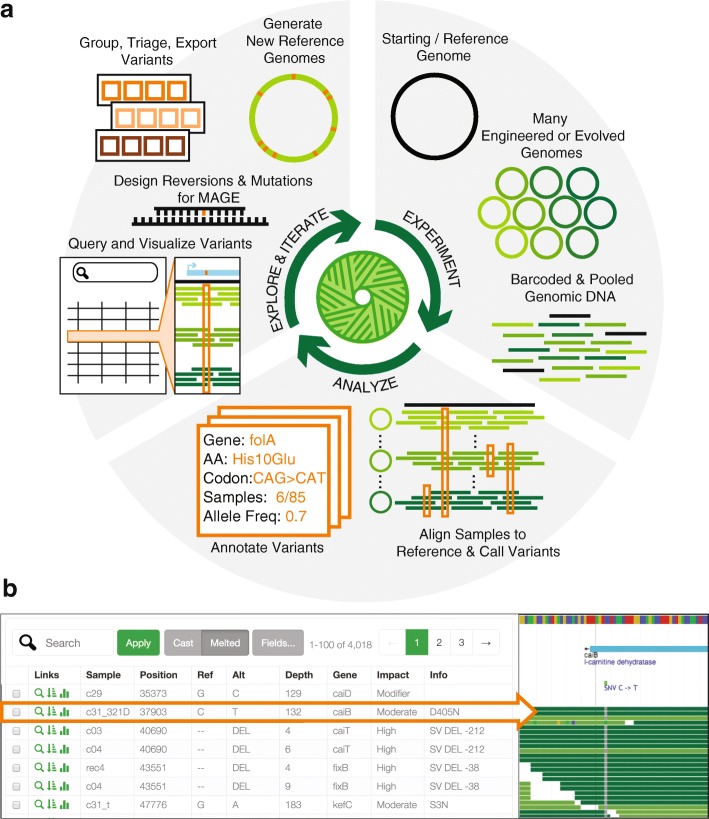
Fig. 1.
Millstone enables rapid iterative multiplex genome analysis and engineering. a To use Millstone, a researcher uploads a reference genome and next-generation sequencing reads for many individual genomic clones, for example from long-term evolution or targeted genome editing. Millstone performs alignment and variant calling for both single nucleotide variants and structural variation and then assigns predicted effects based on reference genome annotations. A unified data model stores sample genotype, phenotype, and variant annotation data. Variants can then be queried, filtered, and grouped into sets for export, triage, and analysis. These variant sets can be used to design oligonucleotides to recreate or revert mutations of interest, or used to generate new versions of the reference genome. b A combined screenshot of the Millstone analysis and alignment visualization views (condensed and cropped for clarity). A custom query language and a corresponding query form in the user interface allow searching and filtering over the data. As variant calls sometimes require visual inspection and comparison, Millstone’s variant analysis view provides programmatically generated links to visualizations of the relevant read alignments in JBrowse [18]