Fig. 4.
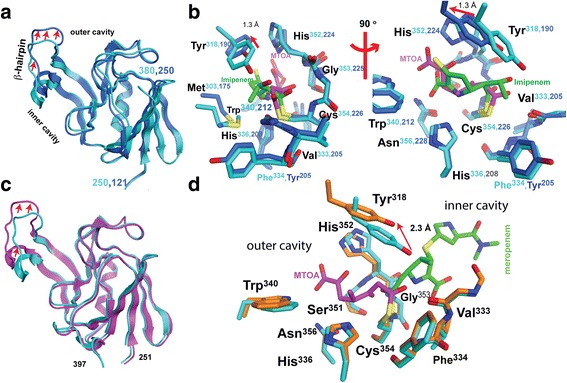
Structural comparison of Mtb Ldts with different carbapenem adducts. a Overlay of catalytic domains of apo-LdtMt1 (colored blue) and apo-LdtMt2 (colored cyan). Red arrows show the displacement of the β-hairpin flap between paralogs. b Two views related by a counterclockwise 90° rotation of the overlay of outer cavity-bound adducts of LdtMt1-imipenem (4VYM; carbon atoms of enzyme and adduct are colored blue and green, respectively) and LdtMt2-MTOA corresponding to the biapenem/LdtMt2 complex structure (colored in cyan and magenta). c Overlay of the LdtMt2 catalytic domains of LdtMt2-meropenem (3VYO; magenta) and LdtMt2-MTOA adduct (cyan). Red arrows show the displacement of the β-hairpin flap between these complexes forming inner- and outer-cavity adducts, respectively. d Overlay of the catalytic site of LdtMt2-meropenem (carbon atoms of the enzyme and the adduct are colored orange and green, respectively) and LdtMt2-MTOA (cyan and magenta). Red arrows in the panels (b) and (d) show the displacement of the conserved Tyr318 on the β-hairpin flap that in LdtMt1-imipenem and LdtMt2-meropenem interacts with the carbapenems hydroxyacetyl substituent, such interaction is loss in MTOA by the elimination of this group after adduct formation
