Fig. 2.
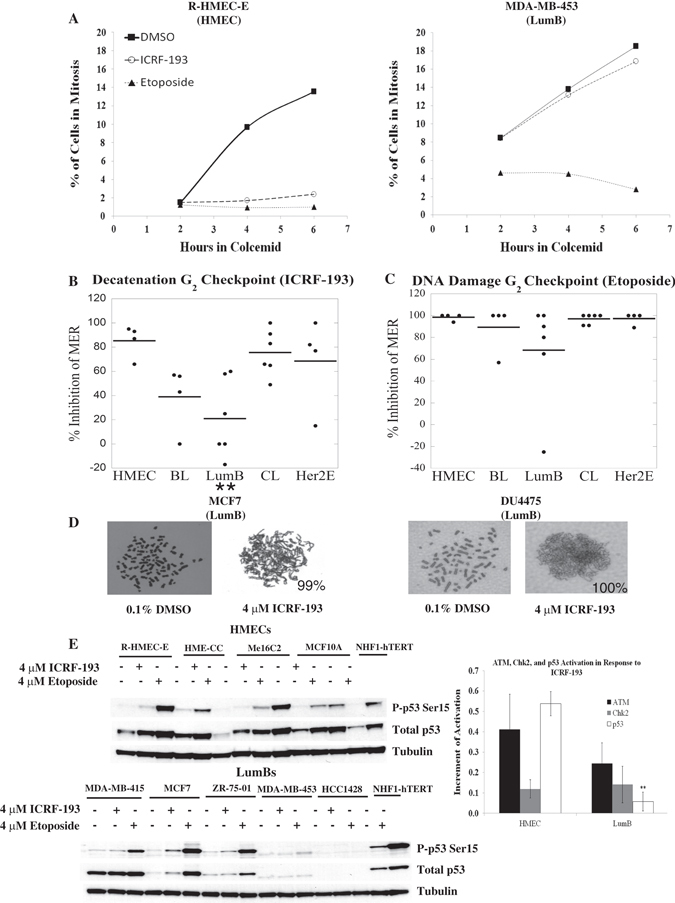
The decatenation G2 checkpoint response is impaired in luminal B (LumB) breast cancer cell lines. A panel of non-tumorigenic immortalized mammary epithelial cell lines (HMEC) and breast cancer cell lines were assessed for G2 and M checkpoint functions using a mitotic entry rate (MER) assay to monitor the rate of the G2/M transition in the presence of the topo II catalytic inhibitor ICRF-193 (decatenation G2 checkpoint) or the DNA-damaging topo II poison etoposide (DNA damage G2 checkpoint). a Example MERs of an HMEC (R-HMEC-E) cell line with effective decatenation and DNA damage G2 checkpoints and a LumB (MDA-MB-453) cell line with a defective decatenation G2 checkpoint. b and c The average percent inhibition of the MER of each cell line grouped according to intrinsic molecular subtype. Each point on the graph represents the average of 3 independent experiments for an individual cell line, and the bold lines represent the class average. d Example metaphases of LumB cell lines in the presence of DMSO exhibiting individualized chromosomes. Severely under-condensed and/or entangled chromosomes were observed in >88% of LumB cells upon treatment with 4 µM ICRF-193, suggesting that ICRF-193 is capable of inhibiting topoisomerase II in LumB cell lines. Percentages of entangled/under-condensed chromosomes are shown in the lower right hand corner of each ICRF-193 treated example. e HMECs activate p-Ser15 p53 after ICRF-193 or etoposide treatment (top panel). The HME-CC etoposide sample displayed aberrant mobility of ATM and reduced expression of p53 which could not be reproduced; therefore, this sample was omitted from the analysis. LumB cell lines exhibit reduced levels of p-Ser15 p53 in response to ICRF-193 (lower panel). Quantification of p53 activation is shown in the right panel. Data are representative of two independent experiments. *p-value < 0.05, **p-value that remains significant when controlling for FDR (5%), BL: basal-like, CL: claudin-low, Her2E: Her2-enriched
