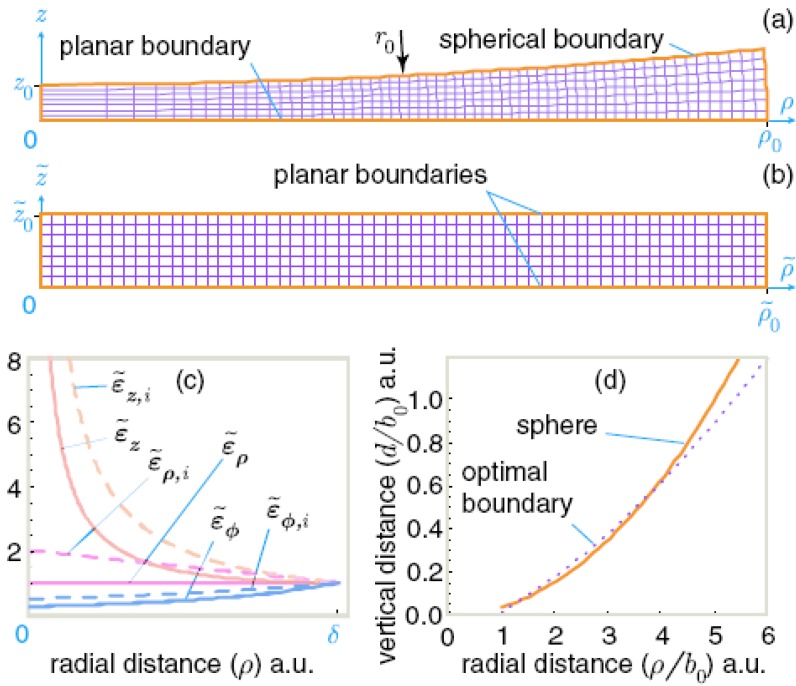
Figure 1.
A space between a spherical surface and a planar surface (a) mapped onto a layer with planar boundaries (b). (c) Distribution of the radial (top), azimuthal (middle), and axial (or vertical) diagonal components of permittivity and permeability in the equivalent planar waveguide. Dashed lines show the same components in the waveguide with a radius-dependent refractive index. (d) Normalized profile of the optimal waveguide shape plotted for a cloak radius of b0 = 172 µm. The shape of the optimal waveguide may be approximated by a spherical surface placed on top of a flat surface, as shown by the dashed line.