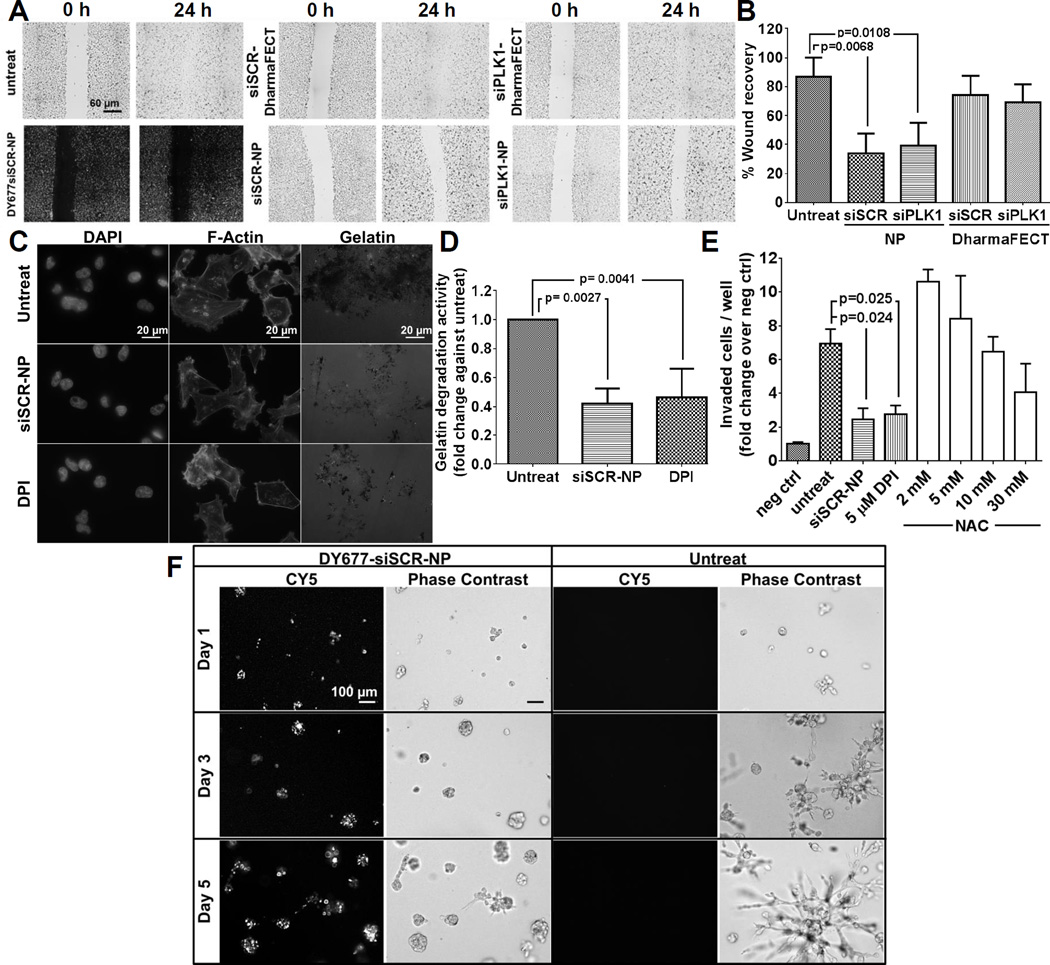
Figure 3.
NP treatment impedes cellular migration and reduces cellular invasiveness of LM2-4luc+/H2N cell line. (A) Representative images of in vitro scratch assay with siSCR or siPLK1 on NP, or on DharmaFECT (all with 50 nM as siRNA). Cells were treated for 24 h prior to wound scratch and images were taken at 0 h and 24 h post-scratch. (B) The percent wound recovery area from (A) using ImageJ. Data are presented as mean ± SD from 3 independent experiments (n=8-10 images/well, duplicate wells per experiment). (C) Representative images from gelatin degradation assay. Cells were pre-treated with 50 nM siSCR-NP or 5 µM DPI prior to seeding on the FITC-gelatin coated coverslips for 24 h. Cells were stained for F-actin and nuclei. (D) The percentage of gelatin degradation per total number of cells in (C) by ImageJ. Data are presented as mean ± SD from 3 independent experiments (n = 5 images/well, >50 cells/field, duplicate wells per experiment). (E) Invasion of LM2-4luc+/H2N cells after 48 h treatment with 50 nM siSCR-NP, 5 µM DPI, or 2–30 mM NAC through Matrigel-coated Boyden chambers, normalized by negative controls (number of cells invaded through chambers with no serum added). Data are represented as mean ± SD from two independent experiments performed in duplicates. (F) Representative images of LM2-4luc+/H2N cells pretreated with 50 nM DY677siSCR-NP prior to seeding in 3D matrigel culture vs. untreat and imaged on day 1, 3, and 5 post-seeding.