Figure 1.
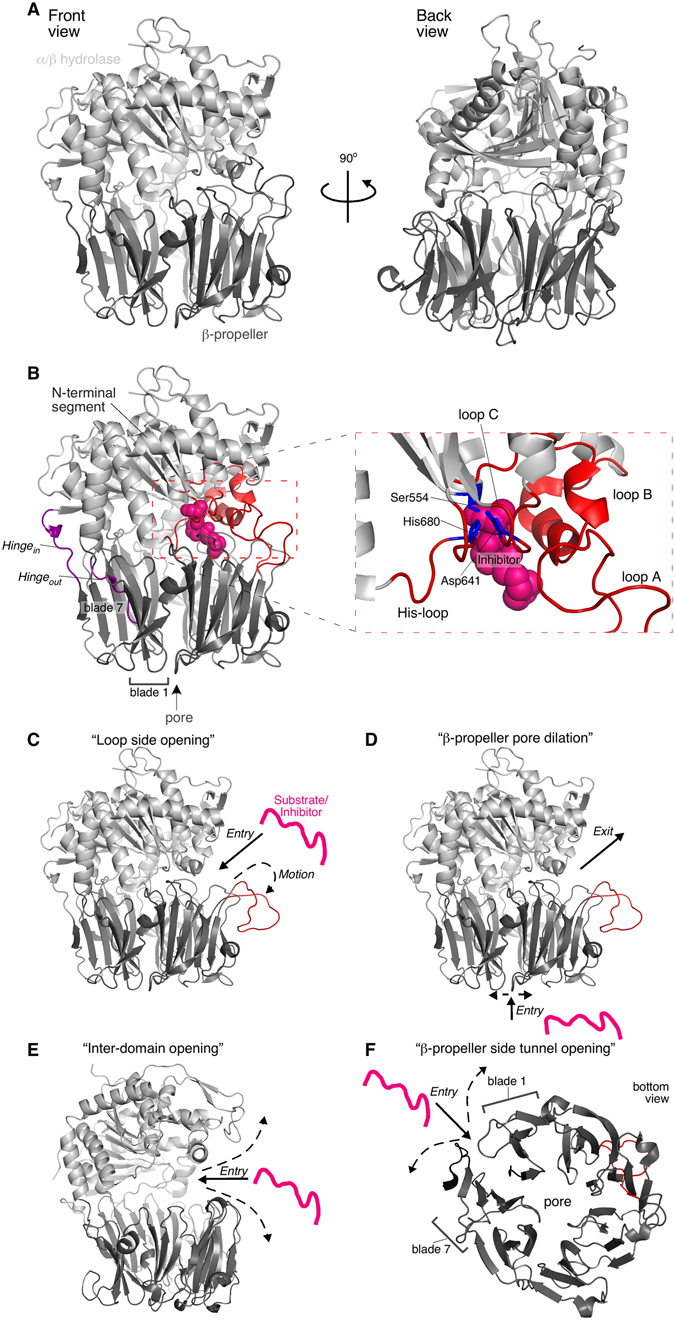
Structure of PREP and current models for the substrate gating and molecular function mechanisms. (A) PREP structure and domain organization (PDB accession entry: 1H2W) in a front (left) and back (right) view. Human PREP and its homologues are two-domain assemblies consisting of an α/β hydrolase domain (light grey) and a 7-bladed β-propeller (dark grey). (B) The two domains are connected through a two-linker hinge (purple). Hinge out connects the N-terminal segment of the α/β hydrolase domain with the first β-propeller β-strand. Hinge in links the last β-propeller strand with the rest α/β hydrolase domain. The catalytic triad in the α/β hydrolase domain comprises of the His680 residue from the His-loop (residues 676–685), Asp641 from loop C (636–646) and Ser554 (right; zoom in view of the active site and its surrounding loops; catalytic triad in blue; loops in red). PREP substrates and its hydrolase inhibitors bind to the active site (PDB accession entry 4AN0; inhibitor KYP-2047 shown as pink spheres). Loops A (189–209) and B (577–608) (red) surround the active site. The propeller-like configuration of the β-blades in the β-propeller domain create a ~4Å-wide pore. The blade unit is 4 antiparallel β-strands. (C–F) Current models for the substrate gating mechanism of PREP. A hypothetical substrate/inhibitor is drawn as a pink line; dash-lined arrows represent motions of PREP regions related to gating; continuous-lined arrows indicate the suggested substrate entry pathway. (C) Loop A (red) has been suggested to move outwards enabling side entry of PREP substrates (PDB accession entry: 1H2W; loop A was manually translated outwards using PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 1.8 Schrödinger, LLC). (D) The β-propeller pore may dilate for substrate encapsulation, while loop A outward motions may provide the exit pathway (structure as in panel C). (E) Bilateral opening of the inter-domain interface by large scale outward motions of both domains around the hinge would expose the active site (PDB accession entry: 4BP8; Trypanosoma brucei Prolyl Oligopeptidase B). (F) The unclosed β-propeller between blades 1 and 7 may provide a side tunnel by weakening interactions between the two β-stranded blades (bottom view of the β-propeller; structure as in panel A).
