Fig. 3.
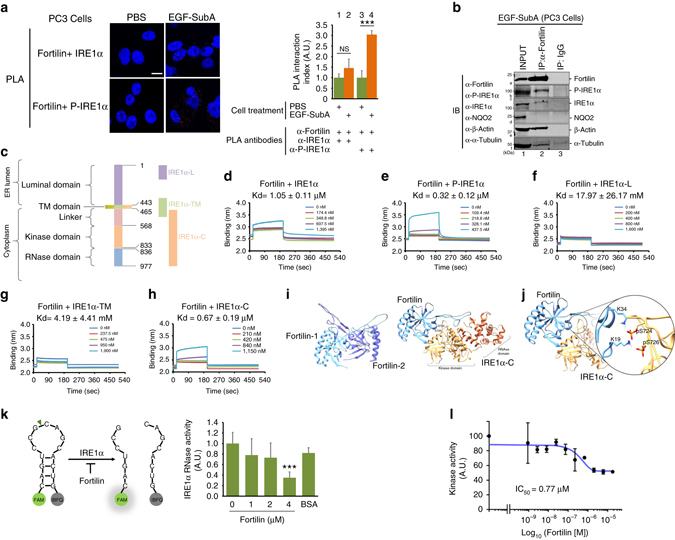
Fortilin interacts with the cytosolic domain of IRE1α and inhibits its protein kinase and RNase activities. a Proximity ligation assay (PLA) shows a specific interaction between fortilin and P-IRE1α in EGF-SubA-treated PC3 cells. The cells were treated with 2 nM EGF-SubA for 24 h and subjected to PLA, using anti-IREα and anti-P-IRE1α antibodies to evaluate fortilin-IRE1α and fortilin-P-IRE1α interaction, respectively. PLA interaction indices were calculated by dividing the number of red dots by the number of nuclei, expressed as means ± s.d. (n = 3), and analyzed by two-tailed unpaired t-test. NS not statistically significant; ***P < 0.005. Scale bar = 10 µm. b Fortilin co-immunoprecipitates P-IRE1α. PC3 cells were treated with 2 nM EGF-SubA for 24 h, lysed and subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP). c Domain structure of human IRE1α. Human IRE1α consists of the ER luminal domain (aa 1–443), transmembrane domain (aa 444–464), linker region (aa 465–567), kinase domain (aa 568–833), and endoribonuclease (RNase) domain (aa 836–997). The following recombinant proteins were used for biolayer interferometry: full-length IRE1α (aa 1-977), IRE1α-Myc-DDK (aa 1–977); IRE1α-L, GST-IRE1α (aa 1–70); IRE1α-TM, GST-IRE1α (aa 401–500); and IRE1α-C, GST-IRE1α (aa 468–977). d–h Fortilin binds to P-IRE1α through its cytosolic domain. Biotinylated fortilin was immobilized to the streptavidin biosensor. Recombinant IRE1α, either full-length or fragment, was applied to the biosensor at various concentrations, and dissociation constants (Kds, expressed as mean ± s.d., n = 3) were derived. i Lowest energy binding pose of fortilin (blue) with cytosolic domain of IRE1α (green) (the right panel) presented with that of a fortilin-fortilin dimer (the left panel). j Intermolecular interactions between phosphorylated serine724 (pS724) and serine726 (pS726) of the cytosolic domain of IRE1α with lysine residues (K19 and K34) of fortilin. k Fortilin inhibits the RNase activity of IRE1α. An in vitro IRE1α RNase activity assay was performed by incubating IRE1α with human recombinant fortilin and the substrate fluorescently tagged XBP1 RNA stem loop, the cleavage of which would allow the fluorescein amidite (FAM) to fluoresce. Data were expressed as means ± s.d. (n = 4) and analyzed by two-tailed unpaired t-test. ***P < 0.005. l Fortilin inhibits the kinase activity of IRE1α. An in vitro IRE1α kinase activity assay was performed by incubating IRE1α with [γ-33P]ATP, recombinant fortilin, and myelin basic protein (MBP) as a substrate of the kinase in the kinase reaction buffer. The phosphorylation index was calculated by dividing the radioactivity of MBP for a given fortilin concentration by that of the vehicle control and expressed as means ± s.d. (n = 2) from which half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) was calculated
