Fig. 4.
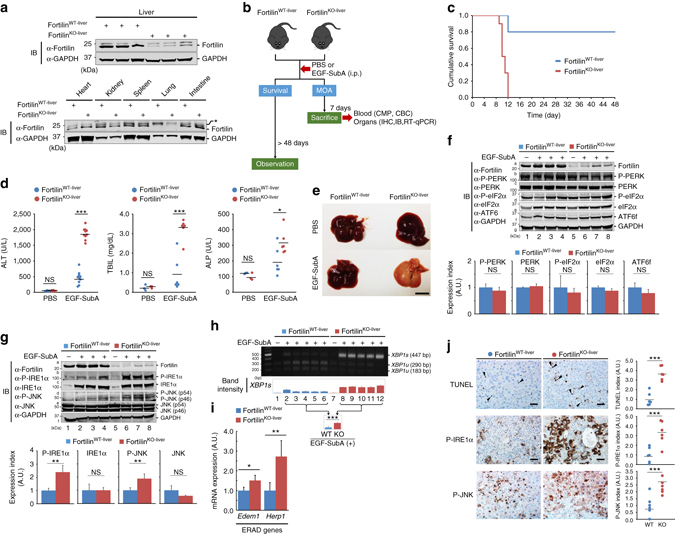
Fortilin protects the whole animal against ER stress-induced liver failure and death by negatively regulating the IRE1α stress sensor pathway. a Liver-specific absence of fortilin in fortilinKO-liver mice. *, non-specific bands. b Experimental protocol. i.p. intraperitoneally, MOA mechanism of action, CMP complete metabolic panel, CBC complete blood count, IHC immunohistochemistry. c Higher survival rates of fortilinWT-liver than fortilinKO-liver mice after EGF-SubA challenge. A Kaplan–Meier survival curve and log-rank test showed the significantly better survival of fortilinWT-liver mice than that of fortilinKO-liver mice (n = 10, P < 0.001). d Massive liver damage of EGF-SubA-treated fortilinKO-liver mice. The sera from fortilinWT-liver and fortilinKO-liver mice, treated with either PBS or EGF-SubA, were assayed for alanine aminotransferase (ALT; n = 5 and 10, for PBS and EGF-SubA, respectively), total bilirubin (TBIL; n = 3 and 6), and alkaline phosphatase (ALP; n = 3 and 6). Data were expressed as mean and analyzed by two-tailed unpaired t-test. NS not statistically significant; *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.005. e Drastic gross pathological change in the liver of EGF-SubA-treated fortilinKO-liver mice. Scale bar = 10 mm. f Fortilin fails to negatively regulate the PERK and ATF6 signaling pathways in the EGF-SubA-challenged liver. The total lysates from the livers of fortilinWT-liver and fortilinKO-liver mice, after the indicated treatments, were subjected to IB. Data were expressed as means ± s.d. (n = 3) and analyzed by two-tailed unpaired t-test. NS not statistically significant. g Fortilin inhibits the IRE1α signaling pathway in the EGF-SubA-challenged liver. Data were expressed as means ± s.d. (n = 3) and analyzed by two-tailed unpaired t-test. NS not statistically significant; **P < 0.01. h Fortilin blocks IRE1α-mediated splicing of XBP1 mRNA in the liver of mice under ER stress. The amounts of XBP1s and XBP1u were quantified by quantitative densitometry. Data were expressed as means ± s.d. (n = 5) and analyzed by two-tailed unpaired t-test. ***P < 0.005. i Fortilin inhibits the expression of XBP1s-inducible genes in the liver of mice under ER stress. Expression levels of ER-associated degradation (ERAD) genes—Edem1 and Herp1—in the liver of EGF-SubA-challenged fortilinWT-liver and fortilinKO-liver mice were quantified by RT-qPCR with normalization against 18S rRNA. Data were expressed as means ± s.d. (n = 4) and analyzed by two-tailed unpaired t-test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. j Fortilin blocks apoptosis and IRE1α pathway activation in EGF-SubA-challenged liver. Paraffin sections from the livers of EGF-SubA-treated fortilinWT-liver and fortilinKO-liver mice were subjected to TUNEL, P-IRE1α, and P-JNK staining using 3,3’-diaminobenzidine (DAB) as a chromogen. Data were expressed as means ± s.d. (n = 6) and analyzed by two-tailed unpaired t-test. ***P < 0.005. Scale bar = 50 µm
