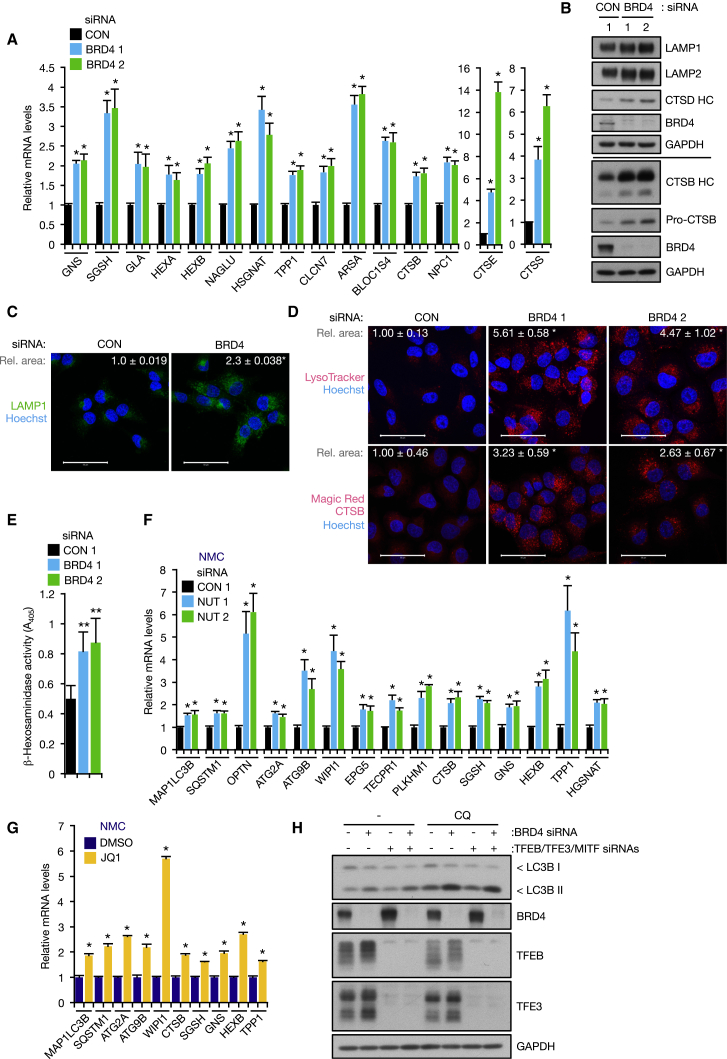
Figure 3.
BRD4 Knockdown Enhances Lysosomal Function
(A) RT-qPCR analysis of KP-4 cells transfected with control or BRD4 siRNA.
(B–D) KP-4 cells transfected with BRD4 siRNA were subjected to western blot analysis with antibodies against lysosomal proteins (B) and stained with LAMP1 antibody (C), LysoTracker Red (100 nM, 2 hr) (D, upper panels), and Magic Red CTSB (1 hr) (D, lower panels). Area of LAMP1+, LysoTracker+, and Magic Red CTSB+ area normalized to cell number is shown (C, CON: n = 115 cells, BRD4: n = 130 cells; D upper, CON: n = 66 cells, BRD4 1: n = 52 cells, BRD4 2: n = 50 cells; D lower, CON: n = 164 cells, BRD4 1: n = 109 cells, BRD4 2: n = 53 cells). Scale bars, 50 μm.
(E) Hexosaminidase activity was measured using lysates from control and BRD4 knockdown KP-4 cells.
(F and G) RT-qPCR analysis of TY-82 cells transfected with NUT siRNA for 72 hr (F) or treated with 500 nM JQ1 for 9 hr (G).
(H) KP-4 cells were transfected with BRD4 and/or MiT/TFE (TFEB, TFE3, MITF) siRNAs and treated with 10 μM CQ for 4 hr.
All data are shown as mean ± SD. In (A) and (F), n = 3 independent experiments. In (E), n = 4 independent experiments. In (G), data are representative of two independent experiments performed in triplicate. ∗p < 0.01, ∗∗p < 0.05. See also Figure S3.