Figure 1.
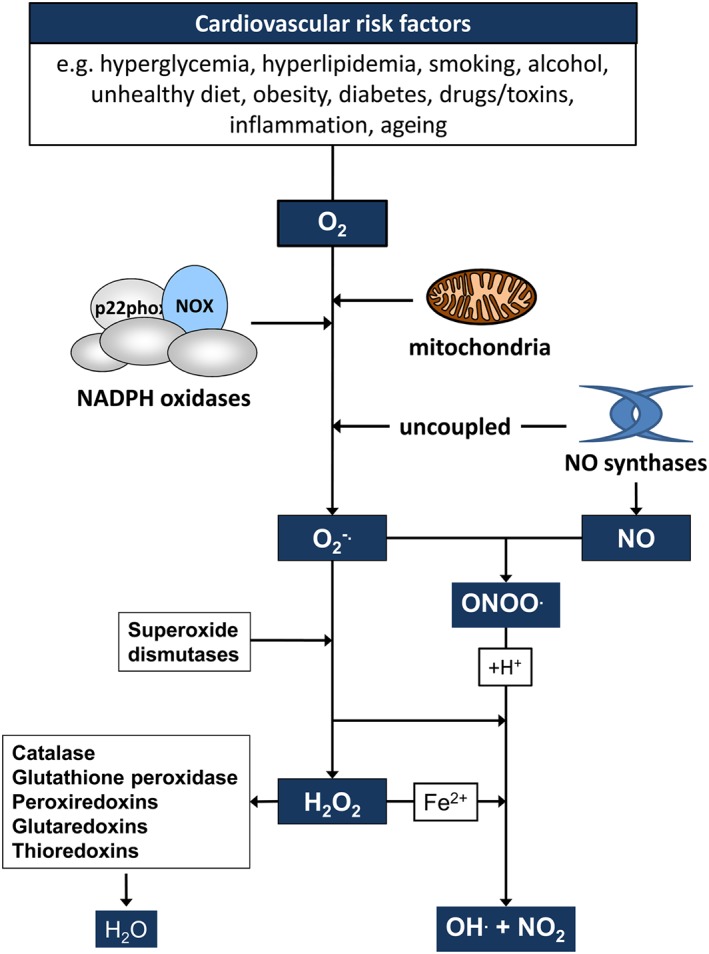
Cardiovascular risk factors promote the generation of ROS. Cardiovascular risk factors have been associated with increased generation of ROS. Superoxide anion radicals (O2 ·−) are generated from molecular oxygen via important sources such as NADPH oxidases, the mitochondrial electron transfer chain and uncoupled NO synthases. O2 ·− can be converted to H2O2 via superoxide dismutases (SOD) or in the presence of NO to peroxynitrite (ONOO−). H2O2 is decomposed or scavenged by catalase, glutathion peroxidase, glutaredoxins, peroxiredoxins or thioredoxins, respectively. O2 ·−, H2O2 and ONOO− can react via different reactions to form hydroxyl anion radicals (·OH) and nitrite (NO2).
