Figure 3.
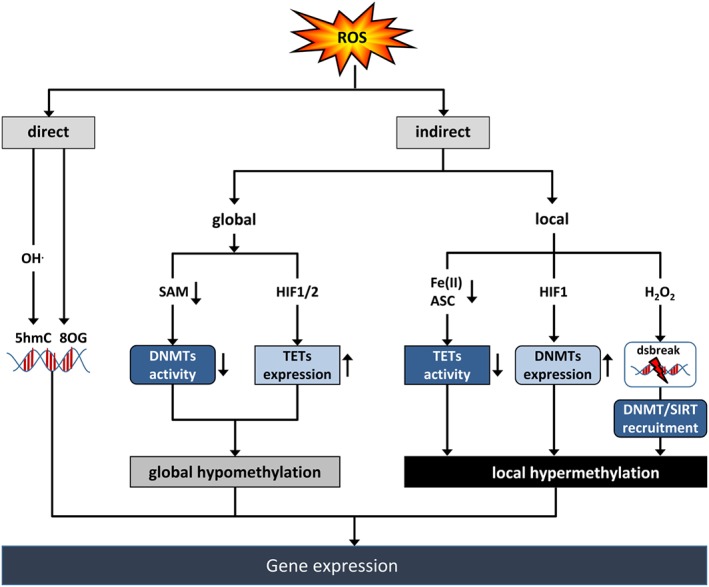
ROS affect DNA methylation. ROS can directly affect DNA by formation of 8‐oxo‐2′‐deoxyguanosine (8OG) or, via hydroxyl radicals (OH−), by formation of 5‐hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC). ROS can also indirectly affect DNA methylation at the global or local level leading to modulation of gene expression. Reduction of the activity of DNA methyltransferases (DNMT) by reducing the availability of SAM or increasing the expression of TET proteins via the transcription factor HIF1 can lead to global hypomethylation. Decreasing TET activity by reducing Fe(II) or ascorbate (ASC) levels, or increasing DNMT expression via HIF1, or recruiting DNMT and the HDM SIRT1 containing complexes to H2O2‐induced DNA double strand breaks (dsbreak) can result in local hypermethylation.
