Figure 1.
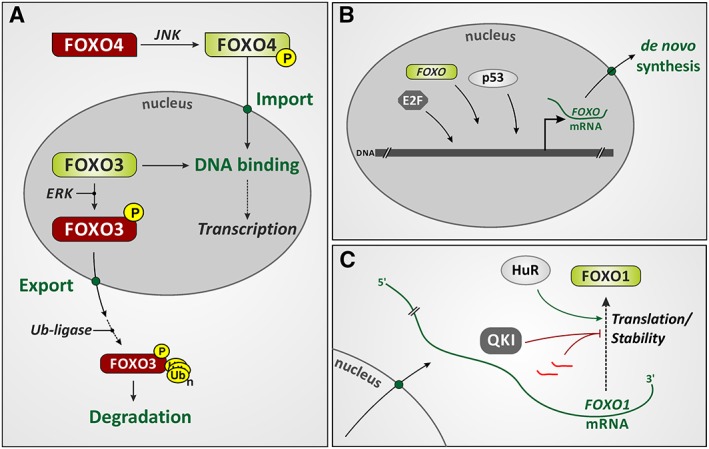
Levels of regulation of FOXO activity and expression. (A) Posttranslational modification of FOXOs affects their activity, subcellular localization and stability. The figure illustrates the effects of phosphorylation of two FOXO isoforms (FOXO3 and FOXO4) by two different kinases, c‐Jun‐N‐terminal kinases (JNK) and extracellular signal‐regulated kinases (ERK). The figure indicates consequences of FOXO phosphorylation: nuclear import and export, respectively, as well as increased or attenuated DNA‐binding activity (red: inactive; green: active FOXO form). A consequence of FOXO3 phosphorylation by ERK is nuclear exclusion and ubiquitination (leading to proteasomal degradation). For further detail regarding FOXO posttranslational modification, see Klotz et al., 2015. (B) Transcriptional regulation of FOXO expression. Transcription factors controlling FOXO expression include certain E2F isoforms, p53 and FOXOs (specifically, FOXO3 regulating FOXO1 expression; see text). (C) FOXO mRNA stability and translation are affected by miRNAs (bright red) and RNA‐binding proteins such as HuR and quaking (see text for details).
