FIG 2.
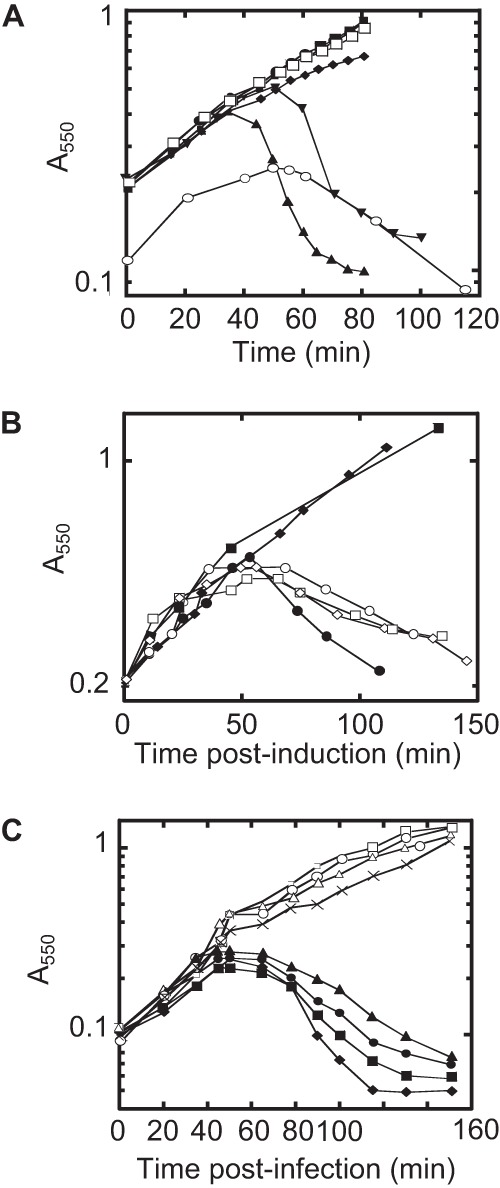
Expression of L from the pQ pRE-L dual-plasmid system is sufficient for lysis. (A) Lysis profile from induction of the dual-plasmid system with MS2 L under the control of the pR′ promoter with 1 mM IPTG or 1 mM IPTG and 0.2% arabinose (Ara) in RY15177 compared to lysis by MS2 infections of RY15177 at an MOI of 5. Cultures were grown at 37°C. Symbols: ●, pQ plus IPTG; ■, pRE-L plus IPTG; ◆, pQ pRE plus IPTG; ▼, pQ pRE-L plus IPTG; ▲, pQ pRE-L plus IPTG plus Ara; □, pQ pRE-L, uninduced; ○, MS2. (B) pcnB alleles are recessive. Induction of plasmid-borne L with IPTG (final concentration of 1 mM) at time zero. Host and plasmid symbols: ●, pcnB+ and vector; ○, pcnB+/pCA24N-pcnB; ■, BMC1 and vector; □, BMC1/pCA24N-pcnB; ◆, BMC2 and vector; ♢, BMC2/pCA24N-pcnB. (C) pcnB alleles confer dominant resistance to MS2 infection. Infection of pcnB alleles with MS2 at an MOI of 5 at time zero. Symbols: ●, pcnB+ and vector; ■, pcnB+/pCA24N-pcnB; ◆, pcnB and vector; ▲, pcnB/pCA24N-pcnB; □, BMC1 and vector; ○, BMC1/pCA24N-pcnB; Δ, BMC2 and vector; ×, BMC2/pCA24N-pcnB. The BMC1 and BMC2 pcnB mutations are defined in the legend to Fig. 3. This image was adapted from reference 14 with permission.
