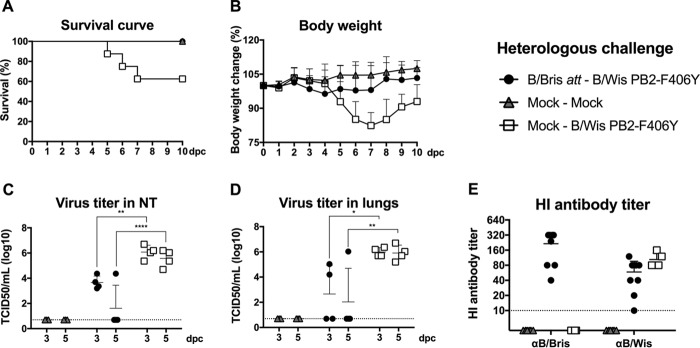
FIG 7.
Protective efficacy of the B/Bris att virus against challenge with the antigenically heterologous B/Wis PB2-F406Y virus. Six-week-old female DBA/2J mice were inoculated i.n. with PBS (mock-vaccinated negative control) or with 106 EID50 of the B/Bris att virus. Three weeks postinoculation, mice were challenged either with PBS (mock) or with 107 EID50 of the B/Wis PB2-F406Y virus by the i.n. route. (A and B) The survival rate (A) and percentage of change in body weight (B) following challenge with the B/Wis PB2-F406Y virus were monitored daily. (C and D) Virus replication and tissue tropism of the B/Wis PB2-F406Y virus in the respiratory tracts of vaccinated (B/Bris att) or negative-control (mock-vaccinated) mice after challenge. At 3 and 5 dpc, four animals from each group were euthanized, and virus titers in the upper respiratory tracts (nasal turbinates) (C) or lower respiratory tracts (lungs) (D) of mice were determined by standard TCID50 assays in MDCK cells. (E) Serum antibody responses in mice measured by HI assays against the homologous (B/Bris) and heterologous (B/Wis) viruses at 21 dpc. Plotted data represent means ± standard errors. Two-way ANOVA was performed to calculate P values. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ****, P < 0.0001.