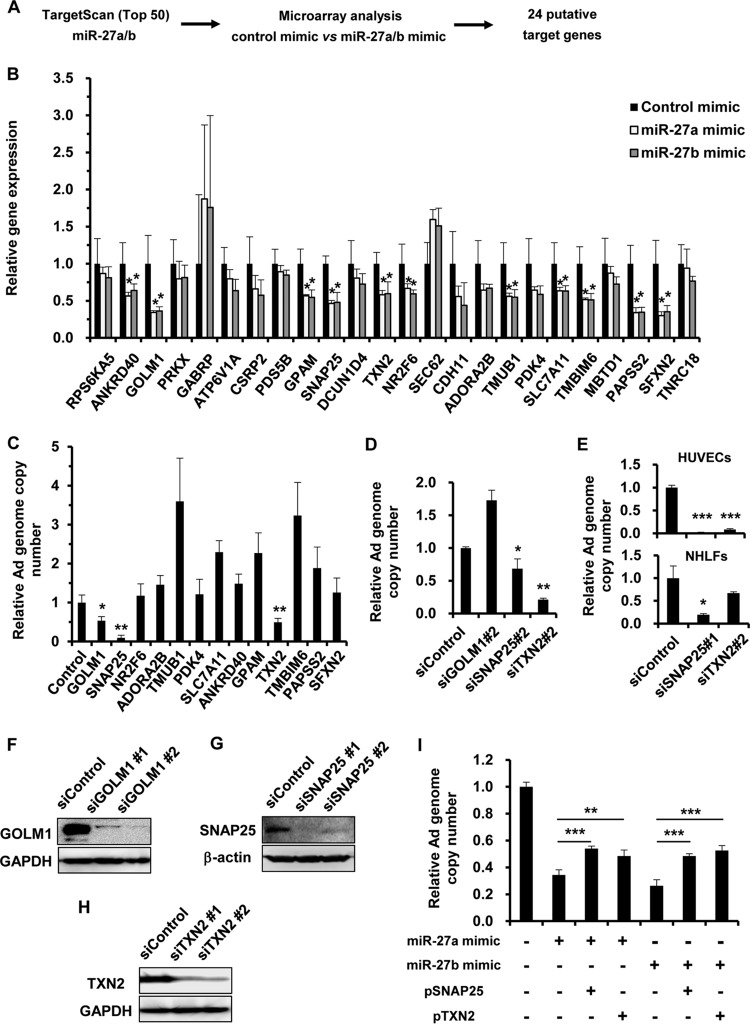
FIG 2.
Identification of miR-27a/b target genes involved in Ad infection. (A) Work flow for the identification of miR-27a/b target genes. Microarray and in silico analyses were performed for the identification of miR-27a/b target genes. (B) HeLa cells were transfected with miR-27a/b mimics at 20 nM. After 48 h of incubation, expression levels of the putative target genes were determined by quantitative RT-PCR analysis. (C to E) HeLa cells (C and D), HUVECs (E), and NHLFs (E) were transfected with the indicated siRNAs at 50 nM, followed by infection with WT-Ad at 100 VP/cell. After 24 h of incubation, the copy numbers of WT-Ad genomic DNA in the cells were determined by quantitative PCR analysis. The data are expressed as means and SD (n = 3 or 4). (F to H) HeLa cells were transfected with the indicated siRNAs at 50 nM. After 48 h of incubation, GOLM1 (F), SNAP25 (G), and TXN2 (H) protein levels were determined by Western blotting. (I) HeLa cells were cotransfected with miR-27a/b mimics and a SNAP25- or TXN2-expressing plasmid (pSNAP25 or pTXN2), followed by infection with WT-Ad at 100 VP/cell. After 24 h of incubation, the copy numbers of WT-Ad genomic DNA in the cells were determined by quantitative PCR analysis. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.