FIG 4.
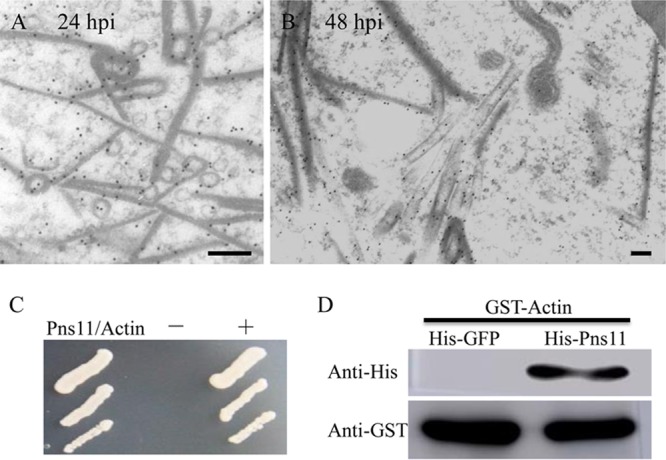
Interaction of Pns11 of RGDV with cytoplasmic actin of R. dorsalis. (A, B) Subcellular locations of Pns11 in recombinant baculovirus-infected Sf9 cells at 24 hpi (A) and 48 hpi (B). Sf9 cells were immunolabeled with Pns11-specific IgG as primary antibodies, followed by treatment with 15-nm gold particle-conjugated goat antibodies against rabbit IgG as secondary antibodies. Bars, 100 nm. (C) A yeast two-hybrid assay was used to detect the interaction of Pns11 and cytoplasmic actin of R. dorsalis. Transformants on an SD-Trp-Leu-His-Ade agar plate are shown. +, positive control, i.e., pBT3-STE and pOstl-NubI; −, negative control, i.e., pBT3-STE and pPR3-N; Pns11/Actin, pBT3-STE-Pns11 and pPR3-N-actin. (D) A pulldown assay was used to analyze the interaction of Pns11 and cytoplasmic actin of R. dorsalis. Pns11 was fused with His to act as bait protein with GFP as a control. Cytoplasmic actin of R. dorsalis was fused with GST as a prey protein. Actin bound to His-fused Pns11 of RGDV but did not bind to His-fused GFP.
