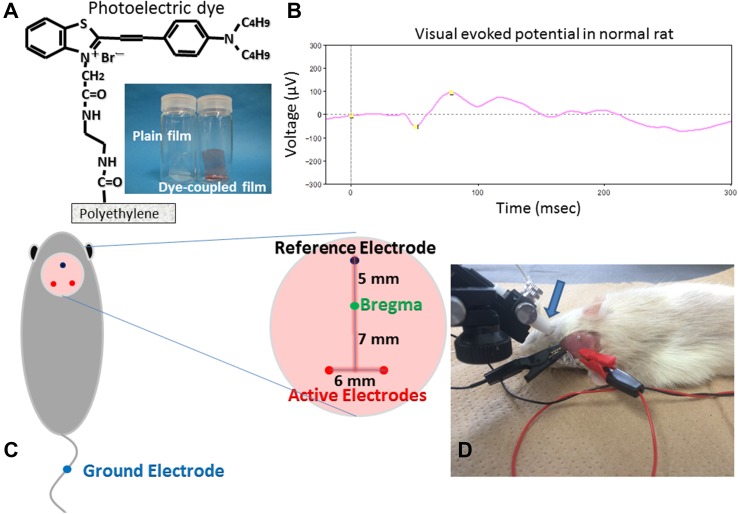
Fig. 1.
Plain polyethylene film and photoelectric dye-coupled polyethylene film, with molecular structure of the dye (a). Visual evoked potential (b) in normal Wistar rat at 6 weeks of the age by photic stimuli (0.5 Hz, 64 summation) of 1000 cd/m2, 10 μs = 0.01 cds/m2 in the background of 0 cd/m2 after overnight dark adaptation. Cranial electrodes (c) on rat’s head to record visual evoked potential. Light stimulation by contact lens light-emitting diode (LED) and visual evoked potential recording (d)