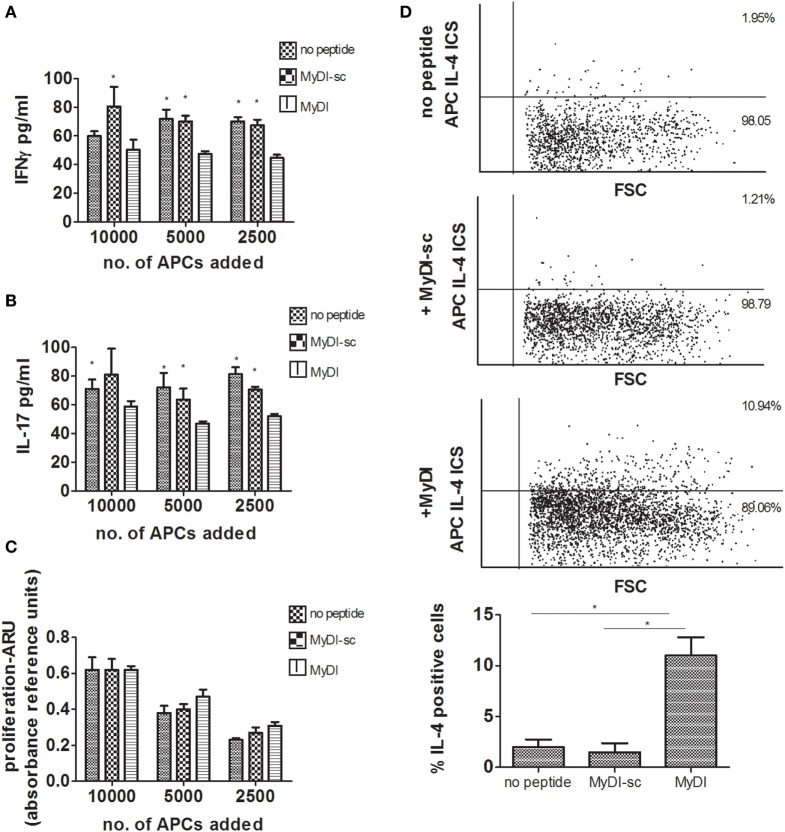
Figure 4.
Peptide inhibition of myeloid differentiation factor 88 in primary human antigen-presenting cells (APCs) leads to a shift in cytokine production by responding T cells. Primary monocytes were isolated from buffy coats and differentiated to macrophages for 6 days. Donor mismatched human CD4+ T cells were isolated from buffy coats and activated by incubation with decreasing concentrations of macrophages pretreated with or without MyDI/MyDI-sc (80 µM). After 6 days of incubation, production of IFNγ (A) and IL-17 (B), and proliferation (C), were determined. Asterisks represent statistical comparison between the specified group vs. treatment with the MyDI peptide. For panels (A,B), one representative experiment of three independent experiments is shown. In panel (C), the proliferation of the three experiments was combined. Intracellular IL-4 expression was determined by flow cytometry (D). One representative experiment of three independent mixed lymphocyte reaction (MLR) experiments is shown in the dot plots, and the average of the three experiments is shown in the bar graphs. The two-tailed t-test was used for statistical evaluation.