Figure 6.
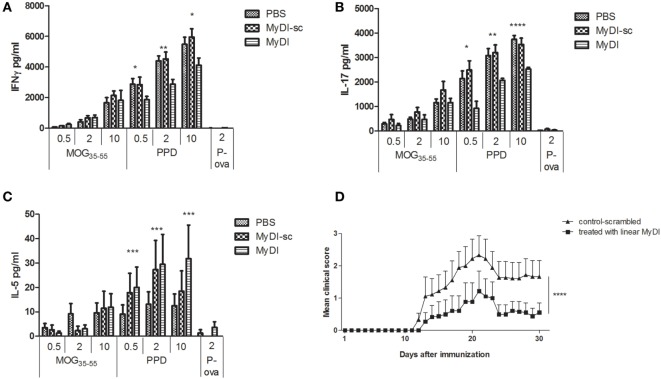
MyDI administration in vivo alters the cytokine profile of responding T cells and ameliorates severity of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). LNC were harvested 11 days after MOG35-55/CFA immunization. Groups were treated at day 0 and every 48 h i.p. with 2 mg/kg MydI, or MyDI-scrambled or PBS as controls. Cells were plated and activated ex vivo with increasing doses of MOG35-55 or increasing doses of purified protein derivative (PPD; 0.5, 2, and 10 µg/mL), or ovalbumin (OVA) peptide (2 µg/mL), an irrelevant antigen control. Cytokines were measured in the supernatants at 72 h. LNC from animals treated with MyDI produced significantly less IFN-γ (A) and IL-17 (B), but significantly more IL-5 (C), at all concentrations of PPD antigen. (A–C) Results are the average of triplicates and the two-tailed t-test was used for statistical evaluation. (D) Mice were immunized with MOG35-55/CFA on day 0, with PTX administration on days 0 and 2. Groups of mice were treated with 2 mg/kg MyDI (squares) or MyDI-sc/PBS (triangles). The graph shows differences in clinical scores between mice treated with MyDI and controls (n = 9 mice per group). Data are mean ± SEM and significantly different by two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA).