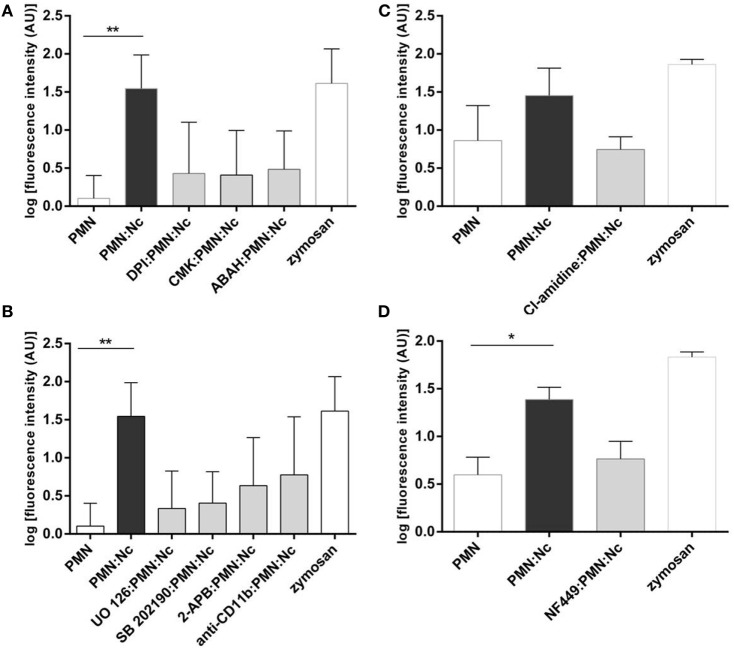
Figure 5.
Functional neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) inhibition assays. Bovine polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMN) were treated with the inhibitors of: (A) NADPH oxidase (DPI, 20 µM), neutrophil elastase (CMK, 1 mM), myeloperoxidase (ABAH, 100 µM), (B) ERK1/2 (UO126, 50 µM), p38 MAPK (SB 203580, 10 µM), SOCE (2-APB, 100 µM), CD11 monoclonal antibodies (diluted 1:5 in PBS), (C) PAD4 (Cl-amidine, 200 µM), and (D) P2Y2 (NF-449, 120 µM) prior to the exposure to tachyzoites (1:2 ratio). Non-treated PMNs were processed in parallel. Following N. caninum tachyzoites exposure, NET formation was determined by quantifying Pico Green®-derived fluorescence intensities (484 nm excitation/520 nm emission wavelengths). Stimulation of PMN with zymosan (1 mg/ml) was used for positive controls, plain medium served as negative control. Each condition was performed in triplicates for each PMN donor (n = 3). Differences were regarded as significant at a level of *p ≤ 0.05 and **p ≤ 0.01.