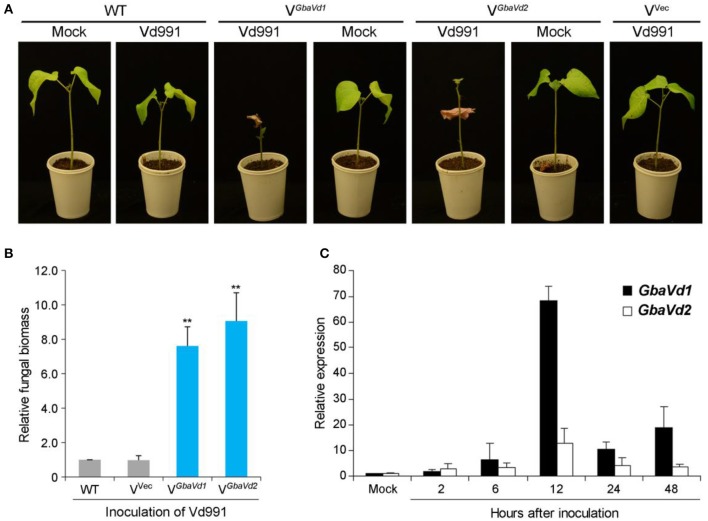
Figure 3.
The GbaVd1 and GbaVd2 genes play essential roles in Verticillium wilt resistance in cotton. (A) Determination of Verticillium wilt resistance in GbaVd1- or GbaVd2-silenced cotton plants. Approximately 14 days after the VIGS procedure in the resistant cotton G. barbadense cv. Hai7124, the GbaVd1- or GbaVd2-silenced plants were inoculated with 5 mL of conidial suspension (2 × 107 conidia/mL) from V. dahliae strain Vd991. The Verticillium wilt phenotypes were determined and photographed 3 weeks after inoculation. WT, the wild type of G. barbadense cv. Hai7124; Mock, inoculation with sterile water; VGbaVd1/VGbaVd2, the GbaVd1- or GbaVd2-silenced plants, respectively; Vvec, VIGS positive control of infiltration with the empty vector pTRV2. (B) Real-time PCR quantification of fungal biomass in GbaVd1- or GbaVd2-silenced plants. Error bars represent standard errors, **significant differences (P ≤ 0.01), according to unpaired Student's t-test. (C) Expression patterns of GbaVd1 or GbaVd2 in cotton after inoculation with V. dahliae. Relative gene quantifications over time were calculated using the comparative threshold (2−ΔΔCT) method, and three independent biological replicates were analyzed. Error bars represent standard errors.