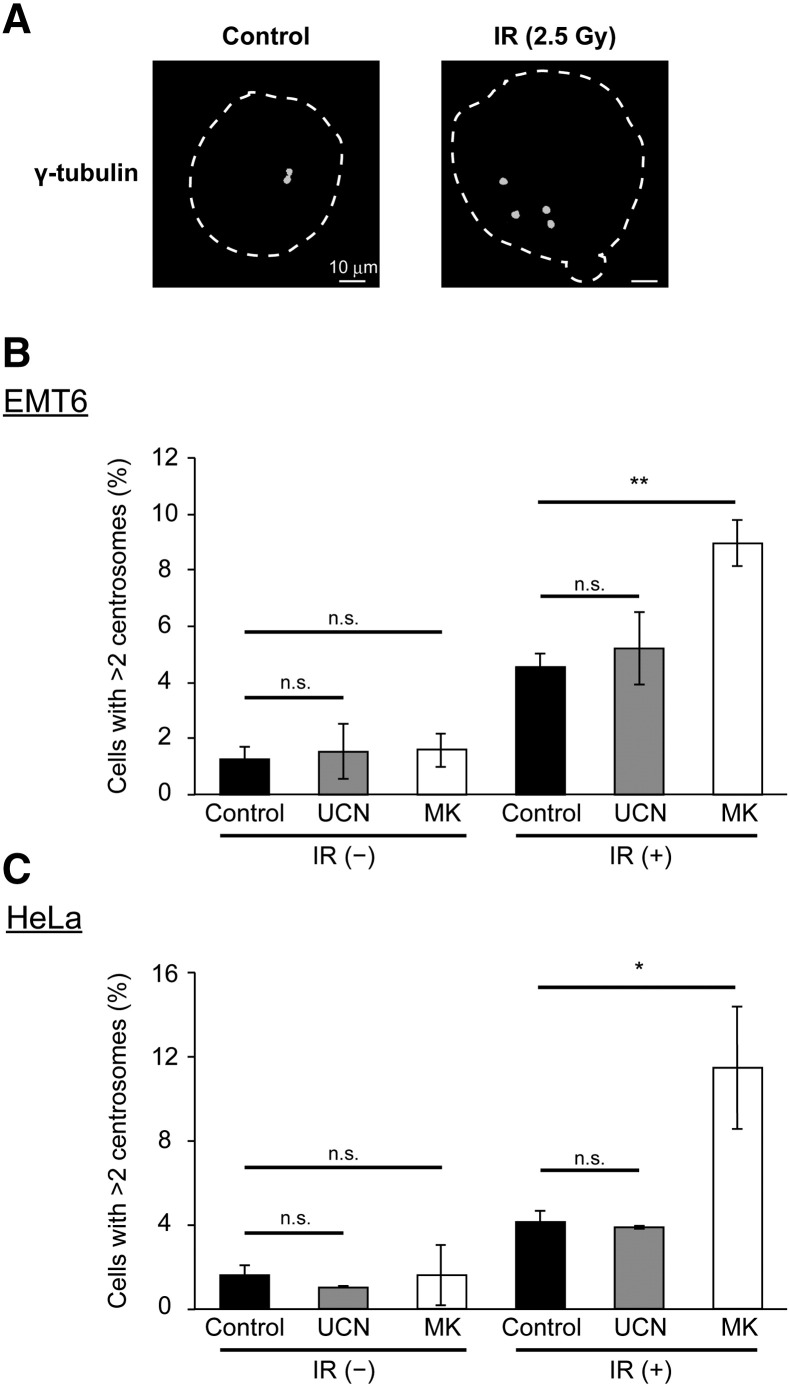
Figure 4.
Effect of Chk1 inhibitors on radiation-induced centrosome abnormalities.
After treatment, centrosome abnormalities were determined by immunostaining with γ-tubulin antibody. (A) Representative images of centrosomes in EMT6 cells with or without X-irradiation. The dashed line represents the nuclear outline. The scale bar represents 10 μm. (B and C) Quantitative analysis of the effect of the two Chk1 inhibitors on centrosome abnormalities. (B) EMT6 cells were X-irradiated at 2.5 Gy and treated with vehicle (white), 5 nM UCN-01 (gray), or 200 nM MK-8776 (white) for 24 h. (C) HeLa cells were X-irradiated at 2.5 Gy and treated with vehicle (black), 10 nM UCN-01 (gray), or 500 nM MK-8776 (white) for 24 h. At least 100 cells were analyzed and the percentage of cells containing more than two centrosomes was determined. Data are expressed as means ± S.D. from three experiments. * P < .05, ** P < .01 vs. Chk1 inhibitors (−) (Student's t-test). n.s., not significant.