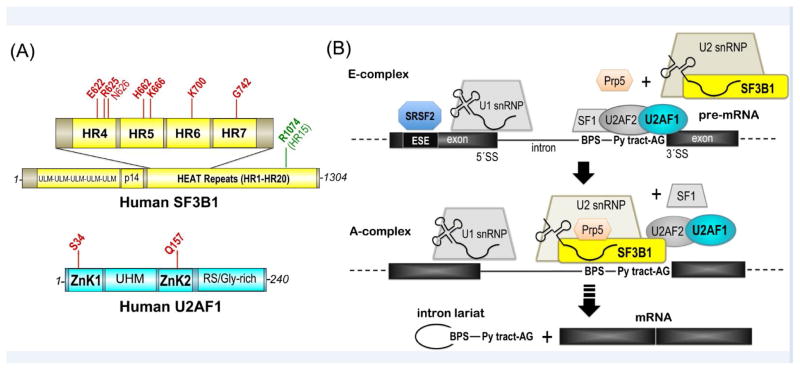
Figure 1.
SF3B1 and U2AF1 domains and functions in pre-mRNA splicing. (A) SF3B1 (top, yellow) and U2AF1 (bottom, cyan) domains and positions of mutational “hotspots” (red) [115, 116]. N626 only recently was classified as statistically significant hotspot across tumors [116] and is shown in lighter font. Mutation of R1074 (green) confers pladienolide-resistance. ULM, U2AF ligand motif; p14, p14-binding site; HR, HEAT repeat motif; ZnK, zinc knuckle motif; UHM, U2AF homology motif; RS/Gly-rich, arginine-serine-rich repeats with poly-glycine stretch. (B) SF3B1 and U2AF1 roles in the early stages of spliceosome assembly at the 3′ splice site. snRNP, small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle; BPS, branch point sequence; ESE, exonic splicing enhancer; Py, polypyrimidine; AG, adenosine-guanosine consensus sequence preceding the 3′ splice site (SS).